Last Updated on April 29, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 6 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 6 maths. In this article, you will find case study questions for CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 9 Symmetry. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 6 Maths Series.
| Chapter | Symmetry |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 6 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Useful for | Class 6 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 6 Maths Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Symmetry
Questions
Mani draws this design on a sheet of paper.
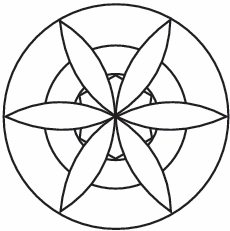
Q. 1. How many lines of symmetry are there in the design?
Sol. There are 12 lines of symmetry.
Q. 2. Gautam modified Mani’s design by erasing all the hexagons from Mani’s design. How many lines of symmetry are there in Gautam’s design?
Sol. Still, there are 12 lines of symmetry.
Q. 3. This is part of the design created by Mani.
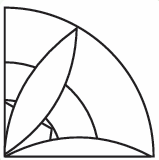
Can you create the complete design by repeating this part? How?
Sol. We can create the full design by repeating this part 5 times.
Q. 4. Mani says, ‘You can have a shape smaller than the one below to make the design.’
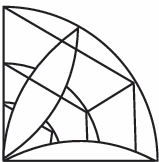
Do you agree? Justify your response.
Sol. Yes, we can reflect the part horizontally and then reflecting the joined parts vertically.
Also check
- The Other Side of Zero Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 10
- Symmetry Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 9
- Playing with Construction Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 8
- Fractions Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 7
- Perimeter and Area Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 6
- Prime Time Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 5
- Data Handling and Presentation Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 4
- Number play Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 3
- Lines and Angles Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 2
- Patterns in Mathematics Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 1
🚀 Boost Your Exam Prep: Get case study questions for all subjects (Class 6-12) now!
👉 Explore more resources on CBSE Class 6
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Symmetry
- Line of Symmetry
- Reflection
- Rotational Symmetry
Case study questions from the above given topic may be asked.
Learning Objectives
- Identify and describe different types of symmetry in various geometric shapes and patterns.
- Locate and draw the line(s) of symmetry in given figures, understanding the concept of symmetry in relation to a dividing line.
- Determine and explain the degree of rotational symmetry in shapes, including identifying the angle of rotation that maps a shape onto itself.
🔗👉 Read Also: NCERT Solutions for Class 1 to 12
Understanding Symmetry
- Symmetry: An object when cut or folded into two halves about a line or axis such that the proportions of both halves are completely balanced is called symmetry. Or we can say that the two halves should be mirror images to each other, and when one half is placed over another, one gets completely superimposed.
- Line of Symmetry: A line that cuts a figure into two parts that exactly overlap when folded along that line is called a line of symmetry of the figure.
- Reflection: Reflection is the phenomenon through which mirror images are formed, and it can be noticed that if an object is placed in front of a mirror, the reflection inside the mirror is purely identical such that all the lengths and angles are same.
A figure that has a line or lines of symmetry is thus also said to have reflection symmetry. - Rotational Symmetry: Rotational symmetry is the number of times a shape can ‘fit into itself’ when it is rotated 360 degrees about its centre.
Symmetry refers to a part or parts of a figure that are repeated in some definite pattern. Symmetry is quite a common term used in day-to-day life. When we see certain figures with evenly balanced proportions, we say, ‘They are symmetrical’.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Symmetry Case Study
Q1: What is symmetry?
A1: Symmetry is a property where one part of a figure is a mirror image of the other part. A figure is said to be symmetrical if it can be divided into two identical halves.
Q2: What is a line of symmetry?
A2: A line of symmetry is an imaginary line that divides a figure into two identical parts, such that one side is the mirror image of the other.
Example: A square has 4 lines of symmetry.
Q3: What are the types of symmetry?
A3: The types of symmetry are:
Line Symmetry: When a figure can be divided into two identical parts by a line.
Rotational Symmetry: When a figure looks the same after being rotated around a central point.
Q4: How many lines of symmetry does a square have?
A4: A square has 4 lines of symmetry:
Two diagonals.
One horizontal line through the center.
One vertical line through the center.
Q5: How many lines of symmetry does a circle have?
A5: A circle has infinite lines of symmetry because it can be divided into identical halves by any diameter.
Q6: What is rotational symmetry?
A6: Rotational symmetry is when a figure looks the same after being rotated by a certain angle around its center.
Example: A square has rotational symmetry of order 4 because it looks the same after being rotated by 900, 1800, 2700, and 3600.
Q7: How many lines of symmetry does an equilateral triangle have?
A7: An equilateral triangle has 3 lines of symmetry.
Q8: What is the difference between a right angle and an acute angle?
A8: A right angle measures exactly 90°, whereas an acute angle is less than 90°.
Q9: What is the difference between line symmetry and rotational symmetry?
A9: Line Symmetry: A figure is divided into two identical parts by a line.
Rotational Symmetry: A figure looks identical after being rotated by a certain angle.
Q10: Can a figure have no lines of symmetry?
A10: Yes, some figures have no lines of symmetry, such as a scalene triangle or an irregular polygon.
Q11: How do you check if a figure is symmetrical?
A11: To check if a figure is symmetrical:
Draw an imaginary line through the figure.
Fold or reflect the figure along the line.
If both halves match perfectly, the figure is symmetrical.
Q12: How many lines of symmetry does a rectangle have?
A12: A rectangle has 2 lines of symmetry:
One horizontal line through the center.
One vertical line through the center.
Q13: What is reflection symmetry?
A13: eflection symmetry occurs when one half of a figure is the mirror image of the other half.
Example: The wings of a butterfly show reflection symmetry.
Q14: Are there any online resources or tools available for practicing “Symmetry” case study questions?
A14: We provide case study questions for CBSE Class 6 Maths on our website. Students can visit the website and practice sufficient case study questions and prepare for their exams. If you need more case study questions, then you can visit Physics Gurukul website. they are having a large collection of case study questions for all classes.



