Last Updated on November 3, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 10 Light – Reflection and Refraction.
| Chapter | Light – Reflection and Refraction |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Useful for | Class 10 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 10 Science Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Light – Reflection and Refraction
Questions
Question 1:
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
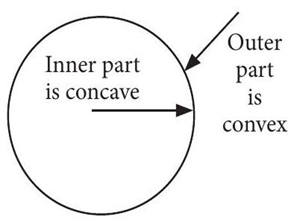
The curved surface of a spoon can be considered as a spherical mirror. A highly smooth polished surface is called mirror. The mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards or outwards is called a spherical mirror. Inner part works as a concave mirror and the outer bulging part acts as a convex mirror. The center of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is called pole and the radius of the sphere of which the mirror is formed is called radius of curvature.
(i) When a concave mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper. What is the name given to the distance between the mirror and carbon paper?
(a) Radius of curvature
(b) Focal length
(c) Principal focus
(d) Principal axis
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance between its pole and principal focus.
(ii) The distance between pole and focal point of a spherical mirror is equal to the distance between
(a) pole and center of curvature
(b) focus point and center of curvature
(c) pole and object
(d) object and image.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: As f=R/2, the distance between pole and focal point of a spherical mirror is equal to the distance between focus point and center of curvature.
(iii) The focal length of a mirror is 15 cm. The radius of curvature is
(a) 15 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 45 cm
(d) 60 cm
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: As f=R/2, R=2f = 30 cm
(iv) The normal at any point on the mirror passes through
(a) focus
(b) pole
(c) center of curvature
(d) any point
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: In a spherical mirror, normal drawn at any point passes through the centre of curvature.
(v) In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at
(a) a flat surface
(b) a bent-in surface
(c) a bulging-out surface
(d) an uneven surface
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at a bulging-out surface.

Question 2:
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
A lens is a piece of any transparent material bounded by two curved surfaces. There are two types of lenses convex lens and concave lens.
Convex lens is made up of a transparent medium bounded by two spherical surfaces such that thicker at the middle and thinner at the edges. Concave lens is also made up of a transparent medium such that thicker at the edge and thinner at the middle. The mid-point of the lens is called optical centre.
A point on the principal axis, where the incident parallel rays meet or appears to come out after refraction is called focus.
A convex lens converges a parallel beam of light to other side whereas concave lens spreads out.
(i) Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in dictionary?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Convex lens is used as magnifying glass. For better performance its focal length should be small.
(ii) Which type of lenes are shown in given figure (a) and (b).

(a)

(b)
(a) Plano concave, concavo convex
(b) Plano convex, convexo concave
(c) Double concave, concave convex
(d) Convexo concave, double convex
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: Plano convex, convexo concave
(iii) A small bulb is placed at the focal point of a converging lens. When the bulb is switched on, the lens produces
(a) a convergent beam of light
(b) a divergent beam of light
(c) a parallel beam of light
(d) a patch of coloured light.
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
(iv) The part of lens through which the refraction takes place is called
(a) aperture
(b) centre of curvature
(c) principal axis
(d) focus
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: Aperture is the area of the lens available for refraction.
(v) A water drop acts as a
(a) convex lens
(b) concave lens
(c) double concave lens
(d) none of these
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (a) is correct.
Explanation: Water droplets behave like a convex lens only as refraction takes place on outer surface.

Also check
- Our Environment Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 14
- Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 9
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 8
- Control and Coordination Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 7
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 4
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 13
- Electricity Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 12
- The Human Eye and the Colourful World Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
- Light – Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10
- Life Processes Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Reflection of Light
- Laws of Reflection
- Real and Virtual Image
- Mirror Formula
- Lens Formula
- Convex and Concave Lens
- Magnification
- Refraction of Light
- Laws of Refraction
- Refractive Index
- Power of lens
This chapter deals with the basic understanding of light. In this chapter we study about reflection and refraction of light phenomenon.

Helpful Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Preparation
- Download 125 Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 220 Important Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 225 Practical Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 65 Important Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 60 Important Diagram Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 150 Most Repeated Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download Chapter Test for CBSE Class 10 Science
Light – Reflection and Refraction (Explained)
🪞 What Happened in the Mirror?
Neha stood in front of her bedroom mirror, tying her ponytail.
She giggled when the reflection did the exact same thing — raising its hand, smiling when she smiled, even blinking at the same time!
“Why does the mirror copy me?” she asked.
Her brother, Arjun, peeked in and replied,
“Because the light coming from you bounces off the mirror into your eyes. That’s how you see your reflection!”
Neha was curious. “So… the mirror is not copying me — it’s just bouncing light back?”
Exactly.
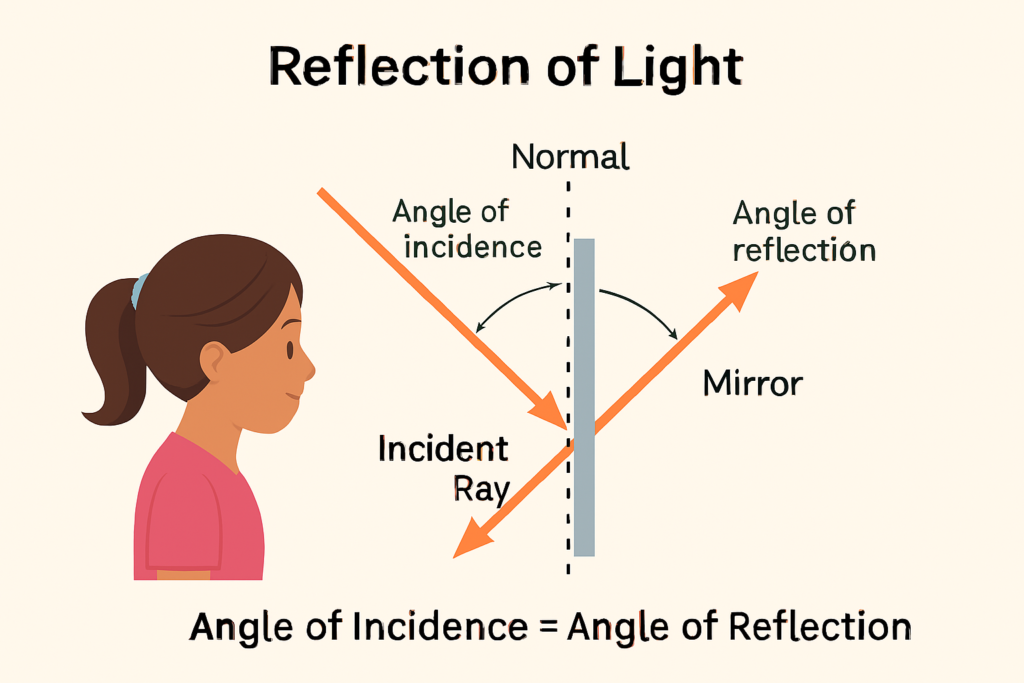
🔍 What Really Happens:
When light hits a smooth surface (like a mirror), it bounces off. This is called reflection.
A ray of light that hits the mirror is called the incident ray.
The one that bounces off is the reflected ray.
And guess what?
They both make the same angle with an imaginary line called the normal.
This is known as the Law of Reflection:
Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection
So, Neha wasn’t really being copied. She was just seeing light doing its magic — bouncing perfectly off the mirror.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Light – Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions
Q1: What are case study questions for CBSE examinations?
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on Light – Reflection and Refraction for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Light – Reflection and Refraction class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of Light – Reflection and Refraction.
Q7: Is light a form of energy?
Ans. Yes, light is a form of energy.
Q8: Do the laws of reflection hold good for spherical mirrors?
A8: Yes, laws of reflection hold good for spherical mirrors.
Q9: What do you understand by reflection of light?
A9: The phenomenon of bouncing back of light to the first medium from the surface of separation of two media is called
reflection of light.
Q10: Is linear magnification always positive?
A10: No, it can be negative also. If the magnification has a plus sign, then the image is virtual and erect.
Q11: For driving a car, what type of mirror would you prefer to see the traffic at your back?
A11: We prefer convex mirror for observing the traffic behind us because its field of view is much larger than the plane mirror. However, it gives erroneous idea about the speed of the vehicles behind us.
Q12: One reads a newspaper due to the light reflected from it. Why then we do not see even faint image of ourselves in the newspaper?
A12: The newspaper causes scattering of light, which is an irregular and diffused sort of reflection. From each point, light goes in all directions. The image is seen only when there is regular refection of light. It is the homogeneous nature of the surface which causes irregular reflection or scattering of light.
Q13: Which part of the eye is reused when one donates the eye?
A13: The cornea of the donor is removed after the death of the person and transplanted in a blind person whose original cornea is opaque. Thus, the blind person gets sight.
Q14: What is meant by refraction of light?
A14: The bending of a ray of light as it passes from one medium to another is called refraction.



