Last Updated on July 7, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Here you will find revision notes for CBSE Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 India – Size and Location. It is a part of Revision Notes for CBSE Class 9 Social Science Series.
| CBSE | Class 9 Geography |
|---|---|
| Useful for | Class 9 Students |
| Subject | Social Science – Geography |
| Chapter | India – Size and Location |
| Type | Revision Notes |
| Covers | Notes Important Keywords Some Interesting Facts About India Mind Map Frequently Asked Questions |
| Important Link | Class 9 Social Science Chapterwise Revision Notes |
India – Size and Location Class 9 Revision Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1
Notes
- India is located in the Northern Hemisphere.
- The latitudinal extent of the Indian mainland is between 8˚ 4´N and 37˚ 6´N and the longitudinal extent is between 68˚ 7´E and 97˚ 25´E.
- The Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea lie to the South-east and the South-west of the Indian mainland, respectively.
- The total area of the Indian land mass is 3.28 million square kilometers.
- The land border of India from the North-east to North-west measures about 15,200 km.
- The total length of the coastline of the mainland, including the Lakshadweep and the Andaman and Nicobar island is about 7516.6 kms.
- India shares its international border with Pakistan and Afghanistan in the North-west.
- China and Nepal are our northern neighbours.
- Bhutan is our North-east neighbouring country while in the east, it is Bangladesh.
- Sri Lanka and the Maldives are the two island nations located in the south.
- India is surrounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east and by the Arabian Sea in the west. Kanyakumari constitutes the southern tip of the Indian Peninsula.
- The Indian subcontinent is a natural geographic unit which comprises the countries of Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, India, Bangladesh and Myanmar.
- India shares its border with all these countries constituting the Indian subcontinent and is involved in border disputes with some countries.
- Politically, India is a federation of 29 states and 7 union territories with New Delhi as its National Capital.
- Being situated at the head of the Indian Ocean, India is connected with the rest of the world by sea in the south and land in the north.
- India is the seventh largest country in the world, in terms of geographical area.
- In size, India accounts for 2.41% of the total geographical area of the world.
- India is nine times the size of Germany and twenty-three times larger than Bangladesh, which is its neighbour in the east.
- Each place on the globe has two types of times – local time and standard time.
- Local time is fixed according to overhead sun while standard time is based on the standard median.
Important Keywords
Peninsula: An area of land surrounded by water bodies on three sides.
Subcontinent: Landmass having distinct physical and cultural identity within the continent.
Strategic Central Location: Nuclear-like existence from where the entire periphery is controlled, manipulated and governed or linked.
Strait: A relatively narrow water way linking two large bodies of water.
Island: A land surrounded on all sides by water bodies.
Indian Union: Refers to the union country of India comprising 29 states and 7 union territories.
Continent: A large area of land that is surrounded or almost surrounded by oceans and that usually consists of several countries.
Coastline: It refers to the line forming the boundary between land and water.
Gulf: A large area of sea partly surrounded by land.
Maritime: Activities of trade and commerce relating to the sea.
Some Interesting Facts About India
- Total Geographical area: 32,87,263 km.
- Newly created state: Telangana with its capital as Hyderabad.
- Longitudinal extent: 68˚7´E-97˚25´E
- Latitudinal extent: 80˚4N–37˚6´N
- North-South distance: 3,200 km.
- Suez Canal: 1869 (opened for trade)
- Largest State: Rajasthan
- Smallest State: Goa
- Standard Meridian of India: 82˚30´E
- Land Frontier: 15,200 km.
Topics to be covered
- Location
- Size
- India and the World
- India’s Neighbours
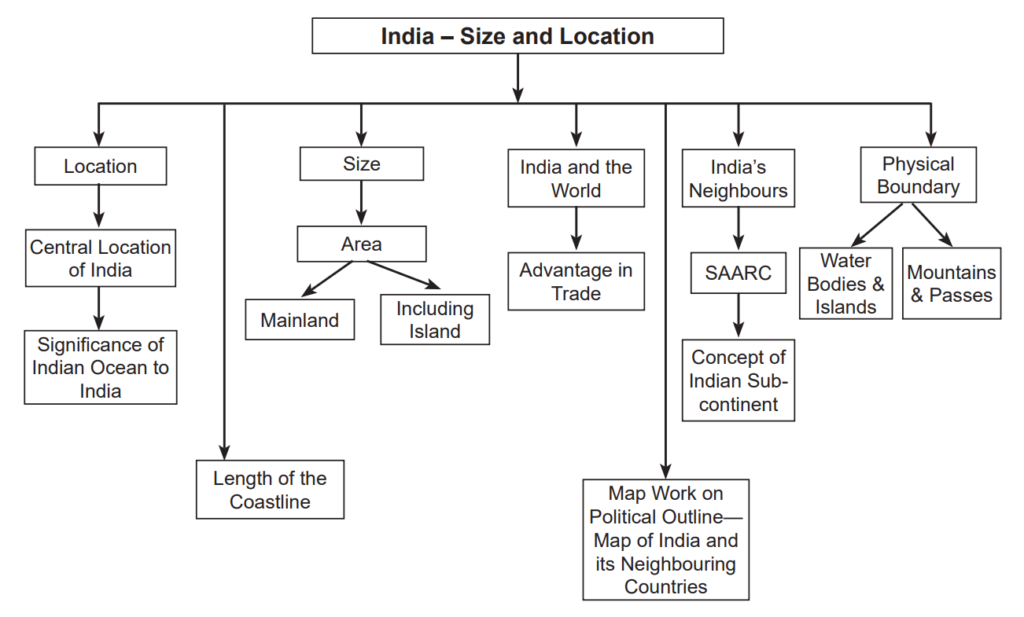
India: Size and Location – Mind Map
Also check
- India – Size and Location Class 9 Revision Notes CBSE Geography Chapter 1
- Forest Society and Colonialism Class 9 Revision Notes CBSE History Chapter 4
- Nazism and the Rise of Hitler Class 9 Revision Notes CBSE History Chapter 3
- Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution Class 9 Revision Notes CBSE History Chapter 2
- The French Revolution Class 9 Revision Notes CBSE History Chapter 1
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on India – Size and Location
Q1: What is the longitudinal extent of India?
A1: The longitudinal extent of India is 68˚7´ E to 97˚25´ E.
Q2: What is the total geographical area of India?
A2: The total geographical area of India is 3.28 million square km.
Q3: Where does India rank in terms of landmass in the world?
A3: India is ranked seventh in terms of landmass in the world.
Q4: What is a subcontinent? What two features that make India a subcontinent?
A4: A landmass with distinct physical and cultural diversity within a continent is called a subcontinent.
Example: India is a subcontinent. Following qualities (features) make India a subcontinent:
(i) India’s self-contained landmass forms a sub-division of the Asian continent.
(ii) It is separated from the Asian continent by the Himalayas in the North, Karakoram mountains in the north-east and Arakan Hills in the east.
Q5: Which countries comprise the Indian subcontinent?
A5: The countries which comprise the Indian subcontinent are:
(i) Pakistan
(ii) Nepal
(iii) Bhutan
(iv) Myanmar
(v) Bangladesh
(vi) India
Q6: What is the difference between a continent and a subcontinent?
A6: A Subcontinent: A subcontinent is a part of a continent. It is an independent geographical unit and separated from the main continent. Example: India.
Continent: A continent is a vast landmass. It stands as a separate physical unit. There are seven continents in the world.
Example: Asia, Australia, North America, South America, Antarctica, Africa and Europe.
Q7: Describe the location of India.
A7: India is the seventh largest country in the world in terms of area. India occupies the central peninsula of Asia. It consists of the mainland and two Island groups, viz., Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea and the Andaman Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal.
Q8: Name the Ocean in the world to be named by our country. Justify the name of the Ocean named after it
A8: The Indian Ocean, the world’s third largest ocean is named after our motherland, India. It is because the subcontinent of India stands at the head of this ocean. The Indian Ocean proves to be a favourite destination of the traders of the world.
Q9: Describe the main features of the Political Division of India.
A9: Political Division of India:
(i) Indian Republic is a union of 29 states (Telangana was the 29th state created in 2014).
(ii) It is the largest democratic country of the world.
(iii) Goa is the smallest and Rajasthan is the largest state.
(iv) Madhya Pradesh is situated in the middle. It is bounded by seven states.
(v) Five states and three union territories are located on the western coast while four states and one union territory are situated on the eastern coast of India.
Q10: Find out the number of Union Territories along the western and eastern coasts.
A10: Union Territories on the Eastern Coast: Pondicherry and Andaman and Nicobar islands.
Union Territories on the Western Coast: Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu and Lakshadweep Islands.
Q11: How can revision notes help in preparing for CBSE Class 9 Social Science exams?
A11: Revision notes are beneficial for CBSE Class 9 Social Science exam preparation in the following ways:
Condensed Information: They provide a concise summary of the chapter, making it easier to review key points quickly.
Focused Study: Highlight important concepts and facts that are crucial for exams, helping to focus study efforts.
Quick Recap: Useful for a quick recap before exams or tests, ensuring all important topics are covered.
Memory Aid: Simplified notes aid in better retention and recall of information during exams.
Q12: What are the benefits of using revision notes for “India – Size and Location”?
A12: The benefits of using revision notes for “India – Size and Location” include:
Enhanced Understanding: Simplified explanations help in better understanding of complex geographical concepts.
Time Efficiency: Saves time by providing all necessary information in one place, avoiding the need to go through the entire textbook.
Improved Performance: Regular use of revision notes can lead to better performance in exams due to better retention of key points.
Easy Accessibility: Handy and can be referred to anytime, anywhere, providing flexibility in study schedules.



