Last Updated on April 29, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 6 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 6 maths. In this article, you will find case study questions for CBSE Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 6 Maths Series.
| Chapter | Fractions |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 6 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Useful for | Class 6 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 6 Maths Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Fractions
Questions
Cross country is a running event in which runners completed a pre-decided distance. It includes different activities in which runners cover different environments. A cross country running event of 11 km is as follows.
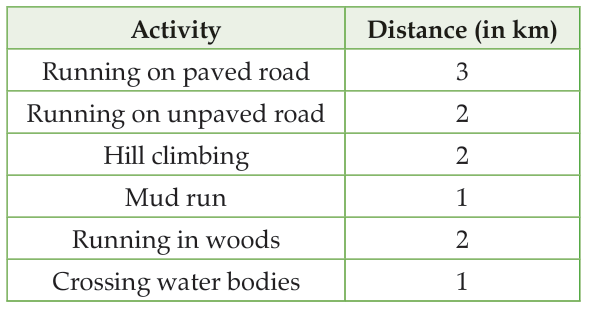
Q. 1. What fraction of the total distance is the mud run?
(a) 11/1
(b) 1/10
(c) 1/11
(d) 1/12
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: 1/11 (total distance = 3 + 2 + 2 + 1 + 2 + 1)
Q. 2. What fraction of the total distance is the distance covered on paved and unpaved roads?
(a) 3/2
(b) 5/5
(c) 5/6
(d) 5/11
Ans. Option (d) is correct
Explanation: 5/11 (paved and unpaved road = 3 + 2 = 5, total distance = 11)
Q. 3. Paul says, ‘By running through woods and climbing hills, half of the total distance in cross country can be covered.’ Is Paul correct? How did you reach the conclusion?
Sol. No, because running on hills and woods covers (2+2 = 4) 4/11 of the distance which is not equal to half of the total distance. (Half of total distance = 11/2)
Also check
- The Other Side of Zero Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 10
- Symmetry Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 9
- Playing with Construction Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 8
- Fractions Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 7
- Perimeter and Area Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 6
- Prime Time Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 5
- Data Handling and Presentation Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 4
- Number play Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 3
- Lines and Angles Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 2
- Patterns in Mathematics Class 6 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 1
🚀 Boost Your Exam Prep: Get case study questions for all subjects (Class 6-12) now!
👉 Explore more resources on CBSE Class 6
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Fractions
- Fractions on the Number Line
- Proper, Improper and Mixed fractions
- Equivalent Fraction
- Simplest form of a fraction
- Like and Unlike Fractions
- Comparing Fractions
- Addition and Subtraction of Fractions
Case study questions from the above given topic may be asked.
Learning Objectives
- Fraction as a part of the whole.
- Fraction on the number line.
- Proper, improper and mixed fractions.
- Equivalent fractions.
- Simplest form of a fraction.
- Comparing like and unlike fractions.
- Addition and subtraction of fractions.
🔗👉 Read Also: NCERT Solutions for Class 1 to 12
Understanding Fractions
A fraction is a number representing a part of a whole. The whole may be a single object or a group of objects. A fraction is represented as Numerator/Denominator where denominator ≠ 0
Fractions can be represented on a number line. Every fraction has a point associated with it on the number line.
In a proper fraction, the numerator is less than the denominator. The fractions, where the numerator is greater than the denominator is called improper fractions. An improper fraction can be written as a combination of a whole and a part and such fraction then called mixed fractions.
Each proper or improper fraction has many equivalent fractions. To find an equivalent fraction of a given fraction, we may multiply
or divide both the numerator and the denominator of the given fraction by the same number.
Fraction is said to be in the simplest (or lowest) form if its numerator and the denominator have no common factor except 1.
Addition and subtraction of fractions is done using similar rules in which the denominators are checked before the addition or subtraction starts. After the denominators are checked, we can add or subtract the given fractions accordingly.
Note:
Proper fraction: numerator < denominator
Improper fraction: numerator > denominator
Mixed fraction: a combination of whole number and fraction.
Fraction is a part of a whole.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Fractions Case Study
Q1: What is a fraction?
A1: A fraction represents a part of a whole. It consists of:
Numerator: The top number, showing how many parts are taken.
Denominator: The bottom number, showing the total number of equal parts.
Example: In 3/4, 3 is the numerator, and 4 is the denominator.
Q2: What are the different types of fractions?
A2: The different types of fractions are:
Proper Fractions: Numerator < Denominator (e.g., 3/5)
Improper Fractions: Numerator ≥ Denominator (e.g., 7/4)
Mixed Fractions: A whole number combined with a proper fraction
Like Fractions: Fractions with the same denominator (e.g., 3/7 and 5/7)
Unlike Fractions: Fractions with different denominators (e.g., 2/5 and 3/4)
Q3: How do you compare fractions?
A3: To compare fractions:
Make the denominators the same (find the least common denominator).
Compare the numerators.
Q4: How do you convert an improper fraction into a mixed fraction?
A4: Divide the numerator by the denominator:
The quotient becomes the whole number.
The remainder becomes the numerator of the fractional part.
Q5: How do you add or subtract like fractions?
A5: For like fractions (same denominator):
Add or subtract the numerators.
Keep the denominator the same.
Q6: How do you add or subtract unlike fractions?
A6: Find the least common denominator (LCM of denominators).
Convert fractions to equivalent fractions with the same denominator.
Add or subtract the numerators.
Q7: How do you multiply fractions?
A7: Multiply the numerators and denominators directly:
Q8: How do you divide fractions?
A8: To divide fractions:
Take the reciprocal of the second fraction (flip numerator and denominator).
Multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction.
Q9: What are equivalent fractions?
A9: Fractions that represent the same value but have different numerators and denominators are called equivalent fractions.
Q10: What is a unit fraction?
A10: A unit fraction is a fraction with 1 as the numerator.
Q11: Why are fractions important in real life?
A11: Fractions are used in:
Cooking (measuring ingredients).
Sharing equally (dividing a pizza).
Construction (measuring lengths).
Q12: Are there any online resources or tools available for practicing “Fractions” case study questions?
A14: We provide case study questions for CBSE Class 6 Maths on our website. Students can visit the website and practice sufficient case study questions and prepare for their exams. If you need more case study questions, then you can visit Physics Gurukul website. they are having a large collection of case study questions for all classes.



