Last Updated on October 13, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
New book for CBSE Class 6 Curiosity, Textbook of Science for Grade 6 learners has been published by NCERT as per National Education
Policy (NEP) 2020. Curiosity, Textbook of Science for Grade 6, comprises twelve chapters. Through the chapters, learners will embark on a journey that will connect them to the world around and spark curiosity for further exploration.
We are providing case study questions for class 6 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 6 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 6 science chapter 8 A Journey Through States of Water.
| Chapter | A Journey Through States of Water |
| Textbook Name | Curiosity |
| Publication Date | July 2024 |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 6 |
| Subject | Science |
| Useful for | Class 6 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 6 Science Chapterwise Case Study |
Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on A Journey Through States of Water
Questions
Passage 1:
Read the given passage below and answer the questions:
The picture shows the four different stages of the water cycle.
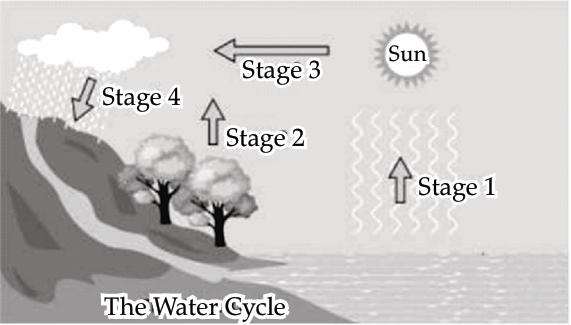
Q. 1. Which stage shows the process of transpiration?
(a) Stage 1
(b) Stage 2
(c) Stage 3
(d) Stage 4
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: Transpiration is the process through which water vapour is released from the leaves of plants into the atmosphere. In the stages of the water cycle, Stage 2 typically represents the process where plants release water vapour through their leaves, thus illustrating transpiration.
Q. 2. In which stage does water vapour condense to form water droplets?
(a) Stage 1
(b) Stage 2
(c) Stage 3
(d) Stage 4
Ans. Option (c) is correct
Explanation: Water vapour condenses to form water droplets during the condensation stage of the water cycle. This is often depicted in Stage 3, where water vapour cools and condenses to form clouds, which eventually result in precipitation.
Q.3. On which day will stage 1 of the water cycle progress the slowest?
(a) A hot and sunny day (b) A cold and sunny day
(c) A hot and cloudy day (d) A cold and cloudy day
Ans. Option (d) is correct.
Explanation: Stage 1 of the water cycle typically involves evaporation. On a cold and cloudy day, the rate of evaporation is slower because the lower temperatures and reduced sunlight decrease the amount of energy available for water to transition from liquid to vapour.
Also check:
- The Wonderful World of Science Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 1
- Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 2
- Mindful Eating Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 3
- Exploring Magnets Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 4
- Measurement of Length and Motion Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 5
- Materials Around Us Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 6
- Temperature and Its Measurement Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 7
- A Journey Through States of Water Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 8
- Methods of Separation in Everyday Life Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 9
- Living Creatures Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 10
- Nature’s Treasures Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 11
- Beyond Earth Class 6 Case Study Questions Science Curiosity Chapter 12
🚀 Boost Your Exam Prep: Get case study questions for all subjects (Class 6-12) now!
👉 Explore more resources on CBSE Class 6
You may also like
Learning Objectives
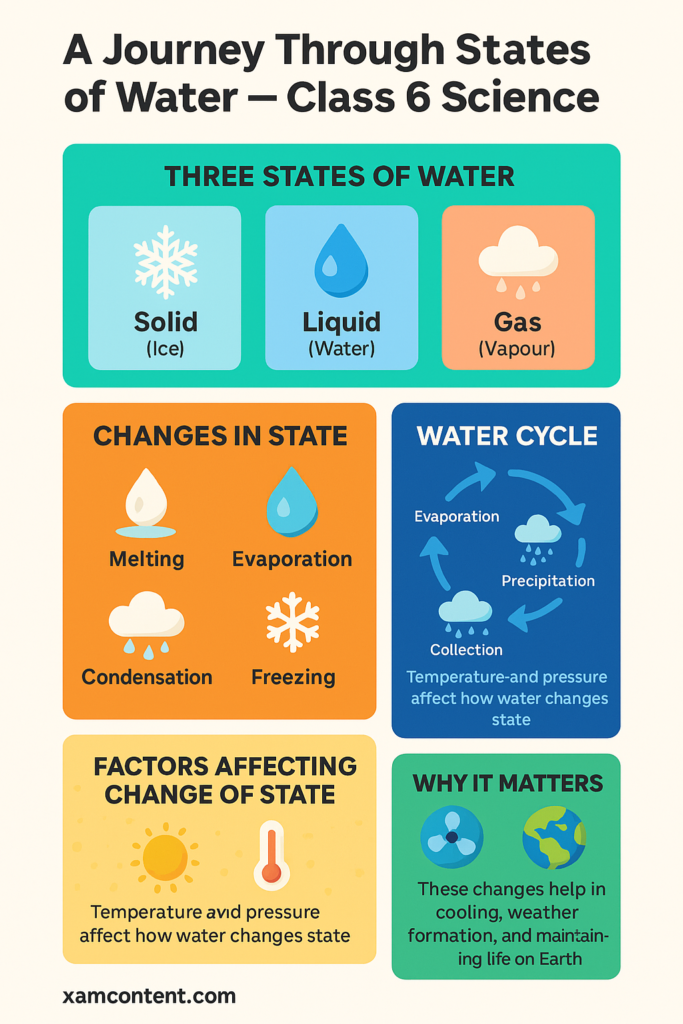
- Explanation of the three states of water (solid, liquid and gas) with real-life examples.
Describing the processes of melting, freezing, evaporation and condensation, including their applications. - Investigation of surface area, temperature and other factors that affect evaporation rates.
- Outlining the stages of the water cycle (evaporation, condensation and precipitation).
Ice melts into water and water freezes into ice, demonstrating they are the same substance.
Dew drops are more visible in the morning because the air cools down overnight. As the temperature drops, the air can no longer hold all its moisture, causing water vapour to condense into tiny droplets on the surfaces of plants.
Keywords Related to A Journey Through States of Water
- Melting: The process by which
solid turns into a liquid when heated. Example: Ice melting into water.
- Freezing: The process by which a liquid turns into a solid when cooled. Example: Water freezing into ice.
- Evaporation: The process where a liquid turns into a gas or vapour, usually due to heat. Example: Water evaporating from a puddle.
- Condensation: The process where a gas turns into a liquid when cooled. Example: Water droplets forming on the outside of a cold drink.
- Surface Area: The measure of the extent of a surface. In the context of evaporation, a larger surface area increases the rate of evaporation.
- Precipitation: Any form of water that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth’s surface, such as rain, snow, sleet or hail.
- Water Cycle: The continuous process by which water moves from the Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back, including processes such as evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
🔗👉 Read Also: NCERT Solutions for Class 1 to 12
Explore More on Chapter 8: A Journey Through States of Water
| A Journey Through States of Water Assertion Reason | A Journey Through States of Water MCQs |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on A Journey Through States of Water Case Study Questions
Q1: What is the new Science textbook “Curiosity” for Grade 6 about?
A1: he new textbook “Curiosity” for Grade 6 Science introduces students to the world of scientific exploration and discovery. It focuses on fostering curiosity and encouraging students to ask questions, observe the world around them, and engage in hands-on activities to understand scientific concepts.
Q2: How is the “Curiosity” textbook different from previous Science textbooks?
A2: “Curiosity” is designed to be more engaging and interactive than previous Science textbooks. It emphasizes inquiry-based learning, where students are encouraged to explore and discover through experiments, observations, and critical thinking rather than just memorizing facts. The textbook is structured around real-world phenomena and everyday experiences to make learning more relevant and exciting for students.
Q3: What are the key themes covered in the “Curiosity” textbook?
A3: The “Curiosity” textbook covers a wide range of themes, including the natural world, physical processes, and basic principles of life sciences. It explores topics such as the properties of materials, the functioning of living organisms, energy, forces, and environmental studies, all while emphasizing the importance of curiosity and inquiry in the learning process.
Q4: How does “Curiosity” support the development of scientific thinking in students?
A4: “Curiosity” supports the development of scientific thinking by encouraging students to ask questions, make observations, conduct experiments, and analyze their findings. The textbook includes activities and projects that help students apply the scientific method, fostering critical thinking, problem-solving, and a deeper understanding of scientific concepts.
Q5: How does “Curiosity” prepare students for higher grades in Science?
A5: “Curiosity” lays a strong foundation for higher grades by introducing students to key scientific concepts and developing their inquiry-based learning skills. By fostering curiosity, critical thinking, and problem-solving abilities, the textbook prepares students for more advanced scientific studies in the middle and high school levels.
Q6: What happens to water when it freezes?
A6: When water freezes, it changes from a liquid state to a solid state, forming ice.
Q7: What is the process called when ice turns into water?
A7: The process is called melting.
Q8: How does water in a puddle eventually disappear?
A8: Water in a puddle eventually disappears due to evaporation, where it turns into water vapour and rises into the air.
Q9: What role does temperature play in the process of evaporation?
A9: Temperature plays a crucial role in evaporation by providing energy to water molecules. Higher temperatures increase the rate of evaporation as more molecules gain enough energy to escape the liquid phase and turn into vapour.
Q10: Are there any online resources or tools available for practicing class 6 science “A Journey Through States of Water” case study questions?
A10: We provide case study questions for CBSE Class 6 Science on our website. Students can visit the website and practice sufficient case study questions and prepare for their exams. If you need more case study questions, then you can visit Physics Gurukul website. they are having a large collection of case study questions for all classes.



