Last Updated on November 3, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 6 Life Processes.
| Chapter | Life Processes |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Useful for | Class 10 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 10 Science Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Life Processes
Questions
Question 1:
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed?
(a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta
(d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
Explanation: Yeast, mushroom and bread mould have a saprophytic mode of nutrition which is chemoheterotrophic in nature. They breakdown complex organic substances by secreting digestive enzyme outside their body and absorb simple molecules as nutrients.
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite?
(a) Yeast
(b) Taenia
(c) Amoeba
(d) Earthworm
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph?
(a) Grass
(b) Mushroom
(c) Amoeba
(d) Paramecium
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves
(a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds
(b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food
(c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants
(d) all of these.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
Explanation: Heterotrophic nutrition is mode of nutrition in which an organism depends on other living organisms for food.
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through
(a) mouth
(b) pseudopodia
(c) cilia
(d) cytostome.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (d) is correct.
Explanation: Feeding apparatus in Paramecium consists of peristome, vestibule, buccal cavity, cytostome (cell mouth) and cytopharynx.

Also check
- Our Environment Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 14
- Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 9
- How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 8
- Control and Coordination Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 7
- Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 4
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 13
- Electricity Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 12
- The Human Eye and the Colourful World Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
- Light – Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10
- Life Processes Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Basic concept of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals.
- Autotrophic Nutrition
- Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Photosynthesis
- Nutrition in Unicellular Organisms
- Human Digestive System
This chapter deals with the basic understanding of nutrition, respiration, transport and excretion in plants and animals. Life Processes are maintenance processes, which sustain orderly structure of living beings e.g. Plants use CO2, animals consume carbohydrate, fats, proteins etc. Continuous supply of energy and materials is needed for maintenance of life by these processes. Life on earth depends on carbon-based molecules, therefore, the sources of energy and materials are carbon-based. The way of life of different organisms depends on complexity of the carbon source. All living organisms use ATP as a source of energy, required for molecular movements, growth and
maintenance of living structure.

Helpful Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Preparation
- Download 125 Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 220 Important Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 225 Practical Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 65 Important Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 60 Important Diagram Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 150 Most Repeated Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download Chapter Test for CBSE Class 10 Science
Life Processes (Explained)

✍️ Story Introduction:
Ravi sat on the balcony, watering his little tulsi plant. Nearby, his dog Bruno panted happily after a morning run. Ravi tilted his head and thought:
“My plant and Bruno are both living… but they look and behave so differently. What makes them both alive?”
His sister, Reema, walked by and smiled,
“Both need to carry out something called life processes, Ravi! That’s what keeps them alive.”
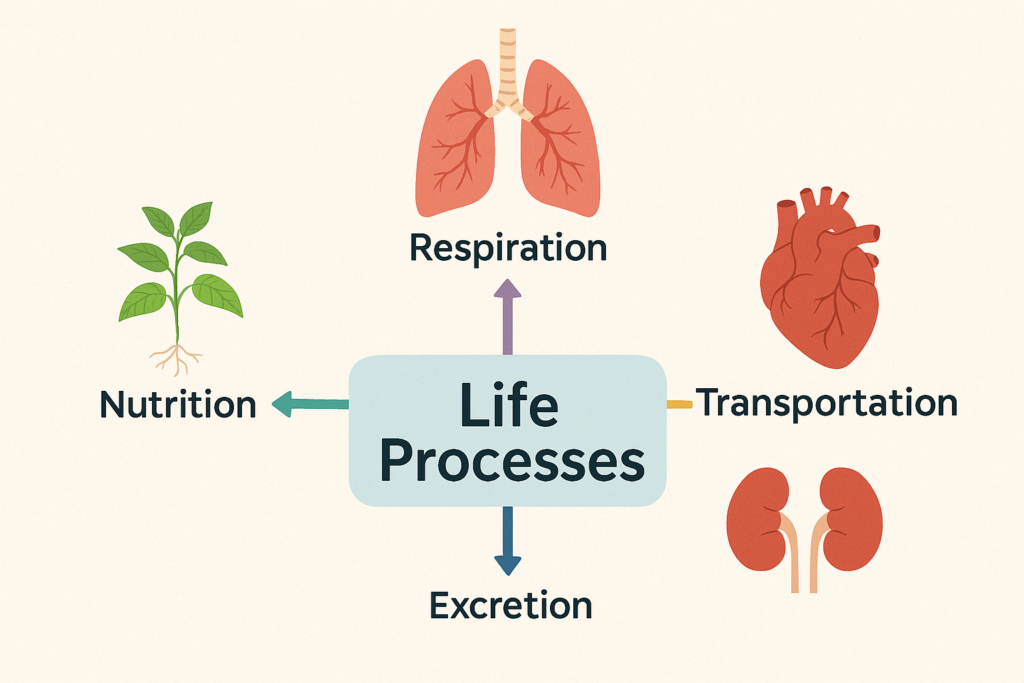
🌱 What Are Life Processes?
Life processes are basic activities that all living organisms perform to survive.
Whether it’s a plant, a dog, or even tiny bacteria — they all:
- Take in food
- Break it down to get energy
- Remove waste
- Grow
- Reproduce
These processes ensure the organism:
- Gets energy for movement and growth
- Maintains its internal balance
- Responds to its surroundings
🧪 Why Are Life Processes Important?
Without these activities:
- Plants wouldn’t grow
- We couldn’t run, think, or even breathe
- Life wouldn’t be possible!
These processes are happening inside you right now, without you even noticing!
All living things perform life processes to survive.
Nutrition, Respiration, Transportation, and Excretion are the main ones.
These keep organisms alive, healthy, and active.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Life Processes Case Study Questions
Q1: What are case study questions for CBSE examinations?
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on Life Processes for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Life Processes class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of Life Processes.
Q7: What is transportation?
A7: Transportation is the life process by which substances absorbed or synthesised in one part of the body are carried to other parts where they are consumed.
Q8: What is circulatory system?
A8: It is the system for transportation of substances within the body consisting of organs and fluids.
Q9: Name the instrument used to measure blood pressure.
A9: Sphygmomanometer
Q10: Why do the ventricles have thicker muscular walls as compared to the atria?
A10: Auricles collect the blood coming from veins with very low pressure and pass it to ventricles. Ventricles pump the blood into various organs of the body. They have thicker muscular walls to create sufficient pressure for pumping the blood.
Q11: What is lymph?
A11: Lymph is the tissue fluid formed by a part of blood that comes out of capillaries into extracellular space. It contains plasma, proteins and blood cells. It serves as a medium for transport of materials to and from individual cells.
Q12: What would be the consequences of deficiency of haemolglobin in our bodies?
A12: Haemoglobin present in red blood corpuscles serves as the respiratory pigment for transport of oxygen. If there
is deficiency of haemoglobin in our body, the blood will not be able to carry sufficient oxygen. This will cause tiredness, shortness of breath and dizziness.
Q13: Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds?
A13: Mammals and birds are warm-blooded animals. To maintain their body temperature they need energy constantly.
To release more energy by aerobic respiration they need more supply of oxygenated blood. Separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in the heart allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body.



