Last Updated on February 18, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
The NCERT Solutions have been updated for 2024-2025 sessions, with the new NCERT Books. All questions are solved with detailed explanation of each and every questions. In this article, we are providing NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat.
| NCERT Solutions | Class 7 Science |
|---|---|
| Session | 2024-2025 |
| Useful for | Class 7 Students |
| Chapter | Heat Chapter 3 |
| No. of Intext Questions | 7 |
| Exercise Questions | 11 |
| Format | Question-Answer Format |
[PDF] Heat Class 7 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 3
NCERT Solutions
INTEXT QUESTIONS
Page-25
Q. 1. Boojho says, “My left hand tells me that the water in mug is hot and the right-hand tells me that the same water is cold. What should I conclude?
Ans. Both conclusions are correct relative to each hand. But a single conclusion cannot be drawn from the given information.
Q. 2. Boojho wondered which of the two scales of measuring temperature he should read.
Ans. Paheli told him that India has adopted the Celsius scale and we should read that scale. The other scale with the range 94-108 degrees is the Fahrenheit scale (oF). It was in use earlier.
Page-26
Q. 3. Paheli measured her body temperature. She got worried as it was not exactly 37oC.
Ans. The temperature of every person may not be 37oC. It could be slightly higher or slightly lower. Actually, what we call normal temperature is the average body temperature of a large number of healthy persons.
Page-27
Q. 4. Boojho got a naughty idea. He wanted to measure the temperature of hot milk using a clinical thermometer. Paheli stopped him from doing so.
Ans. The clinical thermometer is designed to measure the temperature of human body only. The temperature
of human body normally does not go below 35oC or above 42oC. That is the reason that this thermometer has the range 35oC to 42oC whereas the temperature of hot milk is 100oC.
Q. 5. Boojho now understands why clinical thermometer cannot be used to measure high temperatures. But still wonders whether a laboratory thermometer can be used to measure his body temperature.
Ans. The range of clinical thermometer is 35oC to 42oC, hence it cannot be used high temperature. The range of laboratory thermometer is 0oC to 100oC so it can be used to measure body temperature also.
Q.6. Boojho wonders why the level of mercury should change at all when the bulb of the thermometer is brought in contact with another object?
Ans. The temperature of other object may not be the same as that of the bulb of the thermometer. When bulb is brought in contact with that object, the temperature of the bulb changes. So, the level of mercury also changes.
Page-29
Q. 7. Paheli asks: “Does it mean that heat will not be transferred if the temperature of two objects is the same?”
Ans. Energy does transfer between the two bodies continuously even if they are at the same temperature. There is always an exchange of packets of energy at the interface of each and everybody. But there is no net energy transfer between the bodies.
EXERCISE QUESTIONS
Q. 1. State similarities and differences between the laboratory thermometer and the clinical thermometer. [NCERT Ex. Q.1, Page 34]
Ans.
| Laboratory Thermometer | Clinical Thermometer |
| Similarities | |
| In this thermometer, mercury is used. | In this too, mercury is used. |
| In this thermometer, the scale is denoted in Celsius. | In this also, the scale is denoted in Celsius |
| Dissimilarities | |
| Besides body tempera- ture, it is used for mea- suring the temperature of other objects. | This is used only for measuring human body temperatures. |
| Its temperature measuring capacity ranges from 10oC to 100oC | Its temperature measuring capacity ranges from 35oC to 42oC only. |
Q.2. Give two examples each of conductors and insulators of heat.
[NCERT Ex. Q.2, Page 34]
Ans. Conductors: Aluminium and copper. Insulators: Plastic and wood.
Q.3. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The hotness of an object is determined by its _____________
(b) Temperature of boiling water cannot be measured by _____________thermometer.
(c) Temperature is measured in degree _____________
(d) No medium is required for transfer of heat by the process of _____________
(e) A cold steel spoon is dipped in a cup of hot milk. Heat is transferred to its other end by the process of _____________
(f) Clothes of _____________colours absorb more heat better than clothes of light colours.
[NCERT Ex. Q.3, Page 34]
Ans. (a) temperature (b) clinical (c) celsius (d) radiation (e) convection (f) black or dark.
Q.4. Match the following:
| (i) | Land breeze blows during | (a) | summer |
| (ii) | Sea breeze blows during | (b) | winter |
| (iii) | Dark coloured clothes are preferred during | (c) | day |
| (iv) | Light coloured clothes are preferred during | (d) | night |
[NCERT Ex. Q.4, Page 35]
Ans. (i) (d) (ii) (c) (iii) (b) (iv) (a)
Q. 5. Discuss why wearing more layers of clothing during winter keeps us warmer than wearing just one thick piece of clothing.
[NCERT Ex. Q.5, Page 35]
Ans. During winter, when we have so many layers of clothing on our body, the air trapped in between two layers of cloth acts as an insulator. This is the reason why wearing more layers of clothing keeps our body warm in winter as compared to just one thick piece of clothing.
Q. 6. Look at given figure. Mark where the heat is being transferred by conduction, by convection and by radiation.

Ans.
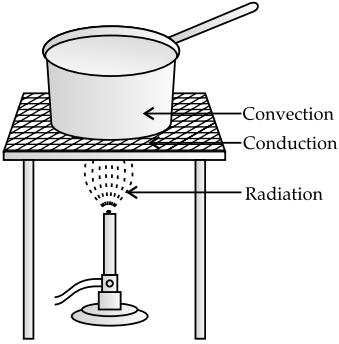
Q. 7. In places of hot climate it is advised that the outer walls of houses be painted white. Explain.
[NCERT Ex. Q.7, Page 35]
Ans. In hot season, the outer walls of the houses should be painted white, because white colour reflects back the heat radiation which falls upon it. That is why the rooms remain cool, they do not warm up in summer.
Q. 8. One litre of water at 30oC is mixed with one litre of water at 50oC. The temperature of the mixture will be:
(a) 80oC
(b) more than 50oC but less than 80oC
(c) 20oC
(d) between 30oC and 50oC
[NCERT Ex. Q.8, Page 35]
Ans. Option (d) is correct.
Q. 9. An iron ball at 40oC is dropped in a mug containing water at 40oC. The heat will:
(a) flow from iron ball to water.
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
(c) flow from water to iron ball.
(d) increase the temperature of both.
[NCERT Ex. Q.9, Page 36]
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
Q. 10. A wooden spoon is dipped in a cup of ice cream. Its other end
(a) becomes cold by the process of conduction.
(b) becomes cold by the process of convection.
(c) becomes cold by the process of radiation.
(d) does not become cold.
[NCERT Ex. Q.10, Page 35]
Ans. Option (d) is correct.
Q. 11. Stainless steel pans are usually provided with copper bottoms. The reason for this could be that
(a) copper bottom makes the pan more durable.
(b) such pans appear colourful.
(c) copper is a better conductor of heat than the stainless steel.
(d) copper is easier to clean than the stainless steel.
[NCERT Ex. Q.11, Page 36]
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
Also check
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
NCERT Solutions are available on many different websites, but they are not updated. we update our content regularly so that student be prepared as per the latest syllabus and pattern. In this NCERT Solution series, we are providing latest solutions for class 6 to 12 new NCERT Books.
- Class 7 Science Chapter 4 Acids, Bases and Salts NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 5 Physical and Chemical Changes NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Respiration in Organisms NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Transpiration in Animals and Plants NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 8 Respiration in Plants NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 9 Motion and Time NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Current and Its Effects NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Light NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Forests: Our Lifelines NCERT Solutions
- Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Wastewater Story NCERT Solutions
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the importance of NCERT solutions for CBSE Class 7 Science?
A1: NCERT solutions are essential for Class 7 Science as they provide detailed explanations to all the questions and exercises given in the NCERT textbook. These solutions help students understand concepts clearly and prepare effectively for exams.
Q2: Are NCERT solutions enough for scoring good marks in Class 7 Science exams?
A2: Yes, NCERT solutions cover the entire syllabus prescribed by CBSE for Class 7 Science. If students thoroughly understand and practice these solutions, they can definitely score well in their exams. However, it’s also beneficial to supplement your studies with additional reference materials and practice questions.
Q3: Where can I find NCERT solutions for CBSE Class 7 Science?
A3: NCERT solutions for Class 7 Science are readily available online on various educational websites, as well as in physical bookstores. Additionally, the official NCERT website provides free access to these solutions. You can also find the best solutions on our website xamcontent.com
Q4: How should I use NCERT solutions effectively for Class 7 Science?
A4: Students should start by thoroughly reading the NCERT textbook chapters. Then, they can solve the exercises and questions given at the end of each chapter. After attempting the questions, they should refer to the NCERT solutions to verify their answers, understand any concepts they find difficult, and learn the correct approach to solving problems.
Q5: Do NCERT solutions for Class 7 Science cover all the chapters equally?
A5: Yes, NCERT solutions for Class 7 Science are designed to cover all the chapters of the textbook equally. Each chapter’s solutions provide detailed explanations and answers to all the questions and exercises given, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the syllabus.
Q6: Are NCERT solutions for Class 7 Science helpful for competitive exams?
A6: While NCERT solutions primarily cater to the CBSE curriculum, they also provide a strong foundation in science concepts, which can be beneficial for various competitive exams. However, for specific competitive exams, students may need to supplement their preparation with additional study materials tailored to those exams’ syllabi and patterns.
Q7: Do these NCERT solutions updated as per latest syllabus?
A7: Yes, These NCERT Solutions have been updated for 2024-2025 sessions, with the new NCERT Books. All questions are solved with detailed explanation of each and every questions.
Q8: What are the learning objectives of the chapter “Heat”?
A8: Learning objectives-
(i) Identify cold and hot objects.
(ii) Define temperature.
(iii) Describe how temperature can be measured using thermometer.
(iv) Describe different types of thermometers.
(v) Explain different ways of heat transfer.
(vi) Explain how woolen clothes keep us warm.
Q9: What are the important keywords from CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat?
A9: Important keywords from CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 3 Heat given below-
Mercury: It is a metal which is liquid at room temperature.
Temperature: The measure of hotness and coldness of the object.
Conductor: The material that allows the flow of heat or electricity to them easily.
Insulator: The material that does not allow the flow of heat or electricity to them.
Kelvin, Fahrenheit and Celsius are the units of temperature


