Last Updated on December 17, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class Class 8 Science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class Class 8 Science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class Class 8 Science chapter 9 The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions.
| Chapter | The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Useful for | Class 8 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 8 Science Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions
Case Study 1: Density Determination of an Irregular Solid (Based on Activity 9.7)
A student performs an experiment (Refer Activity 9.7) to determine the density of an irregularly shaped metal key. The mass of the key is first measured using a digital weighing balance (Activity 9.3) after taring the instrument with the watch glass, yielding a mass of 45.5 g. Next, a 100 mL measuring cylinder (Activity 9.5) is filled with water to the 50 mL mark (V1). The key is slowly lowered into the cylinder using a thread until it is fully submerged. The water level rises and settles at the 58 mL mark (V2). The student carefully reads the final volume by aligning their eye level with the bottom of the meniscus.
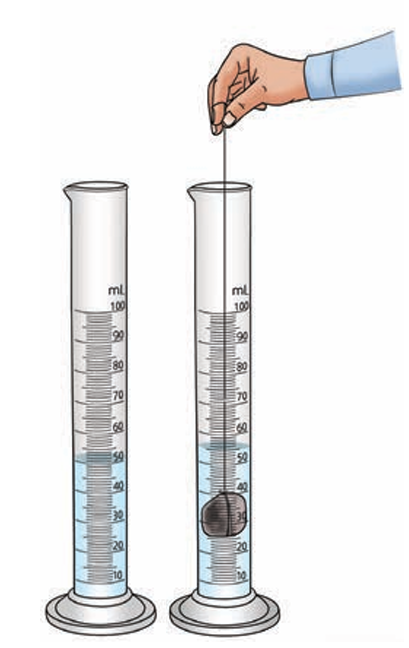
Questions
Q1. The process of resetting the digital balance to zero after placing the watch glass (Fig. 9.12b) ensures the student measures which quantity?
A. The weight of the stone in Newtons.
B. The density of the stone in kg/m3.
C. The mass of the stone in grams.
D. The relative density of the stone.
Q2. Define the fundamental concept used to calculate the volume of the irregular object in this setup.
Q3. Calculate the density of the metal key in g/cm3.
Q4. If the student used 45.5 g of cooking oil instead of the key, and poured it into the 100 mL measuring cylinder, would the resulting oil layer float or sink beneath the water? Justify your prediction using the calculated density of the key and relevant information from the sources.
Answers
A1. C. The mass of the stone in grams.
Explanation: Placing the watch glass and then pressing the tare or reset button brings the reading to zero. When the object (stone/key) is subsequently placed on the watch glass, the reading displayed provides the mass of the object itself, measured in grams (g), as digital balances typically show values in mass units.
A2. Definition: The volume of the irregular object is determined by the water displacement method. The volume of the object is equal to the volume of water displaced, which is found by subtracting the initial water volume (V1) from the final volume (V2).
A3. Answer: 5.6875 g/cm3 Step-by-step Calculation:
1. Calculate the Volume of the Key (V): Volume of displaced water (V) = Final Volume (V2) – Initial Volume (V1)
V = 58 mL − 50 mL = 8 mL
2. Convert Volume Units: The volume in mL is equivalent to the volume in cm3.
V = 8 cm3
3. Calculate Density (D):
Density = Mass / Volume Mass (M) = 45.5 g
D=45.5 g/8 cm3
D=5.6875 g/cm3
A4. The oil layer would float on top of the water.
Explanation: Whether an object floats or sinks is partially determined by its density relative to the liquid. Water has a density of approximately 1 g/mL (or 1 g/cm3) at room temperature. The sources suggest that oil (like the example shown in Figure 9.11, where 1 litre weighs 910 g) is less dense than water. If the oil is less dense than the water it is poured into, the oil will float on the surface
We hope the given case study questions for The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions Class Class 8 helps you in your learning.
Also check
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Our Home: Earth, a Unique Life Sustaining Planet Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 12 How Nature Works in Harmony Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Keeping Time with the Skies Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Light: Mirrors and Lenses Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 9 The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Particulate Nature of Matter Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Exploring Forces Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Health: The Ultimate Treasure Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 2 The Invisible Living World Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Exploring the Investigative World of Science Case Study Questions
🚀 Boost Your Exam Prep: Get case study questions for all subjects (Class 6-12) now!
👉 Explore more resources on CBSE Class 8
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Definition of solutions
- Solute and solvent examples
- Types of solutions
- Concentration and solubility
- Factors affecting solubility
- Saturated and unsaturated solutions
- Everyday examples
Solutions are homogeneous mixtures where the solute is evenly distributed in the solvent.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions Case Study Questions



