Last Updated on January 20, 2026 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for Class 8 Science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for Class 8 Science. In this article, you will find case study questions for CBSE Class 8 Science chapter 12 How Nature Works in Harmony.
| Chapter | How Nature Works in Harmony |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Useful for | Class 12 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 8 Science Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on How Nature Works in Harmony
We hope the given case study questions for How Nature Works in Harmony Class 8 helps you in your learning.
Case Study 1:
Researchers conducted a study (Refer NCERT Activity 12.3) to understand how aquatic life influences terrestrial vegetation. They observed two distinct ponds: Pond A, which contained fish, and Pond B, which had no fish. The researchers noted that the number of dragonflies was significantly lower around Pond A compared to Pond B. Conversely, the population of pollinators like bees and butterflies was higher near Pond A. Surprisingly, the study concluded that the flowering plants near Pond A produced significantly more seeds than those near Pond B. This experiment highlights how biotic components interact in complex ways, creating indirect effects within an ecosystem.
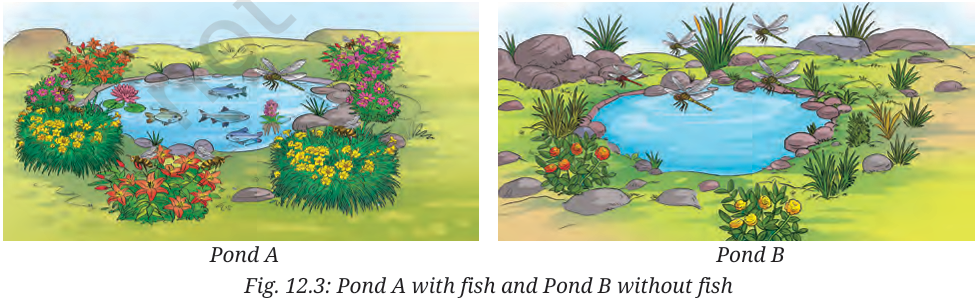
Questions
(i) Based on the feeding relationships observed in this activity, which of the following correctly represents the food chain operating in this ecosystem?
A. Plants → Fish → Dragonflies
B. Plants → Pollinators → Dragonflies → Fish
C. Plants → Fish → Pollinators
D. Dragonflies → Fish → Plants
Question Type: MCQ
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. B. Plants → Pollinators → Dragonflies → Fish
Explanation: Fish eat dragonfly larvae. Dragonflies eat flies, bees, and butterflies (pollinators). These pollinators feed on nectar from plants. Therefore, the flow of energy is Plants → Pollinators → Dragonflies → Fish.
(ii) Explain the biological mechanism behind the observation that plants near Pond A (with fish) produced more seeds than plants near Pond B (without fish).
Question Type: Conceptual
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. The presence of fish in Pond A leads to a decrease in the dragonfly population because fish prey on dragonfly larvae. Since dragonflies are predators of pollinators (bees and butterflies), a reduction in dragonflies allows the pollinator population to thrive. An increased number of pollinators visiting the nearby flowers leads to higher rates of pollination, which directly results in increased seed production for the plants.
(iii) What immediate change would occur in the dragonfly population if fish in Pond A were removed?
Ans. The dragonfly population would increase.
Explanation: The absence of the predator (fish) removes the check on the prey (dragonfly larvae), leading to a higher number of dragonflies in Pond A.
(iv) Figure 12.4 (Refer NCERT) describes the effect of fish on plants as “indirect.” Define this indirect effect in the context of this experiment and contrast it with a direct interaction.
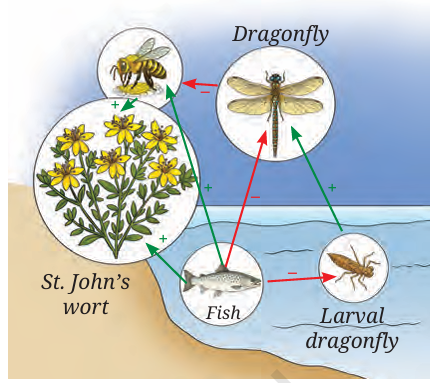
Question Type: Conceptual
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Indirect Effect: An indirect effect occurs when one organism affects another through a third intermediary species, rather than interacting with it face-to-face. In this study, fish benefit the plants not by touching or eating them, but by eating the dragonflies that hunt the plant’s pollinators.
Direct Interaction: This involves physical contact or immediate action, such as the fish eating the dragonfly larvae or the bees collecting nectar from the flowers.
Also check
- Limits and Derivatives Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 12
- Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 11
- Conic Sections Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 10
- Straight Lines Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 9
- Sequences and Series Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 8
- Binomial Theorem Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 7
- Permutation and Combinations Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 6
- Linear Inequalities Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 5
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 4
- Trigonometric Functions Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3
- Relations and Functions Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 2
- Sets Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Chapter 1
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Ecosystems and their components
- Food chains and food webs
- Energy flow in nature
- Symbiotic relationships
- Adaptations and survival
- Human impact on ecosystems
- Sustainability practices
Nature maintains balance through interconnected systems where energy and matter cycle continuously.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on How Nature Works in Harmony Case Study Questions



