Last Updated on December 17, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class Class 8 Science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class Class 8 Science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class Class 8 Science chapter 10 Light: Mirrors and Lenses.
| Chapter | Light: Mirrors and Lenses |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Useful for | Class 8 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 8 Science Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Light: Mirrors and Lenses
Case Study 1: Verifying the Laws of Reflection (Based on Activities 10.4 and 10.5)
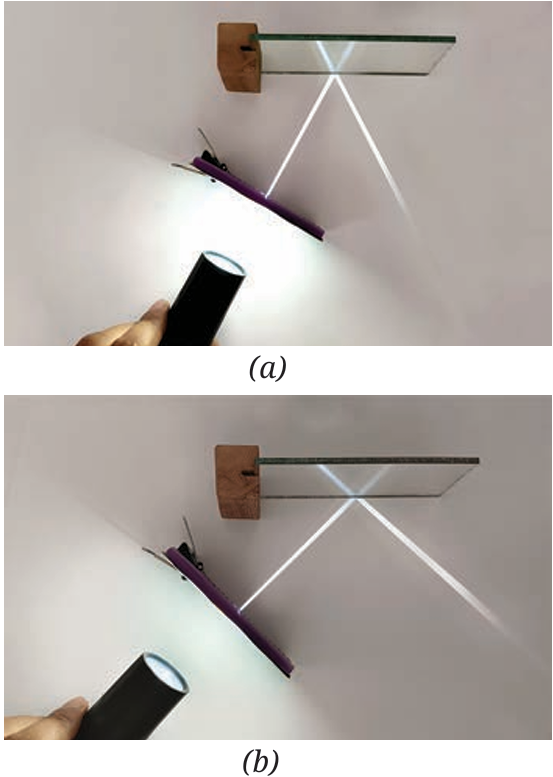
A student performs an experiment to study the reflection of light using a plane mirror (Refer Activity 10.4). They secure a sheet of white paper on a table and place the mirror upright on it. Using a torch and a comb to generate a thin beam of light (incident ray), they direct it onto the mirror surface. To quantify the process, the student draws the normal line, which is perpendicular to the mirror at the point of incidence. In one specific measurement, the incident ray is adjusted such that it makes an angle of 35∘ with the plane mirror surface. Following this, the student extends a piece of chart paper and bends it along the table edge (Activity 10.5), observing that the reflected beam vanishes upon bending the paper.
Questions
Q1. The normal line, used for measuring the angles of incidence and reflection, is defined by its relationship to which surface at the point of incidence?
A. It lies parallel to the incident ray.
B. It lies at 90∘ to the reflecting surface of the mirror.
C. It is the line connecting the incident ray and the reflected ray.
D. It lies along the path of the reflected beam.
Q2. What conclusion about the reflection process is drawn from the observation that the reflected beam disappears when the paper (extended portion) is bent?
Q3. Using the data from the scenario (incident ray makes 35∘ with the mirror surface), calculate the angle of reflection (r).
Q4. If the student adjusts the torch so the incident ray falls exactly along the normal, what is the value of the angle of incidence (i) and what is the path of the reflected ray?
Answers
A1. B. It lies at 90∘ to the reflecting surface of the mirror.
Explanation: The normal is defined as the line drawn from the point where the incident ray strikes the mirror, making an angle of 90∘ to the line representing the mirror (the reflecting surface).
A2. Explanation: This observation demonstrates the second law of reflection. The reflected beam disappears because bending the sheet creates a new plane. This proves that the incident ray, the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence, and the reflected ray must all lie in the same plane.
A3. 55∘
Step-by-step Calculation/Explanation:
1. The normal is drawn at 90∘ to the mirror surface.
2. The angle of incidence (i) is defined as the angle between the incident ray and the normal.
3. Given: The angle between the incident ray and the mirror surface is 35∘.
4. Calculate i: i=90∘−35∘=55∘.
5. According to the first Law of Reflection, the angle of incidence (i) is equal to the angle of reflection (r).
6. Therefore, the angle of reflection (r) =55∘.
A4. Angle of incidence (i) is 00. The reflected ray travels back along the path of the incident ray.
Explanation: The angle of incidence (i) is the angle between the incident ray and the normal. If the incident beam falls along the normal, there is no angular separation between the ray and the normal, meaning the angle of incidence is zero (0∘). By the law of reflection (i=r), the angle of reflection is also 0∘. This forces the reflected ray to travel directly back along the same path as the incident ray.
We hope the given case study questions for Light: Mirrors and Lenses Class Class 8 helps you in your learning.
Also check
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Our Home: Earth, a Unique Life Sustaining Planet Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 12 How Nature Works in Harmony Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Keeping Time with the Skies Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Light: Mirrors and Lenses Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 9 The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Particulate Nature of Matter Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Pressure, Winds, Storms, and Cyclones Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Exploring Forces Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Electricity: Magnetic and Heating Effects Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Health: The Ultimate Treasure Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 2 The Invisible Living World Case Study Questions
- Curiosity Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Exploring the Investigative World of Science Case Study Questions
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Properties of light
- Reflection by mirrors
- Types of mirrors and images formed
- Refraction by lenses
- Concave and convex lenses
- Uses of lenses in instruments
- Human eye basics
Light travels in straight lines and changes direction when reflected or refracted, enabling vision and optics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Light: Mirrors and Lenses Case Study Questions



