Last Updated on November 5, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing assertion reason questions for class 10 computer applications. Assertion reason questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for assertion reason questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise assertion reason questions for class 10 computer applications. In this article, you will find links of assertion reason questions for CBSE Class 10 Computer Applications.
| Subject | Computer Applications |
| Type of Questions | Assertion Reason Questions |
| Other name | AR Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 10 |
| Subject | Computer Applications |
| Unit | All units covered |
| Useful for | Class 10 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
Table of Contents
Click on the chapter to access assertion reason questions
- Introducing Internet Class 10 Assertion Reason Questions Computer Applications Chapter 1
- Internet Services and Mobile Technologies Class 10 Assertion Reason Questions Computer Applications Chapter 2
- Basic HTML Elements Class 10 Assertion Reason Questions Computer Applications Chapter 3
- Computer Applications Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10
- More on HTML Class 10 Assertion Reason Questions Computer Applications Chapter 4
Computer Applications Class 10 CBSE Syllabus
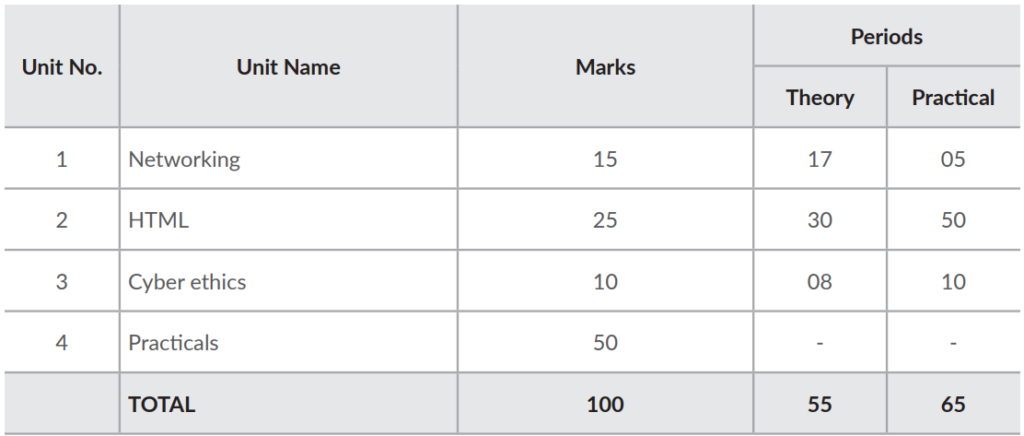
Unit-1: Networking
- Internet: World Wide Web, web servers, web clients, web sites, web pages, web browsers, blogs, news groups, HTML, web address, e-mail address, downloading and uploading files from a remote site.
- Internet protocols: TCP/IP, SMTP, POP3, HTTP, HTTPS. Remote login and file transfer protocols: SSH, SFTP, FTP, SCP, TELNET, SMTP, TCP/IP.
- Services available on the internet: information retrieval, locating sites using search engines and finding people on the net;
- Web services: chat, email, video conferencing, e-Learning, e-Banking, eShopping, e-Reservation, e-Governance, e-Groups, social networking.
- Mobile technologies: SMS, MMS, 3G, 4G.
Unit-2: HTML
- Introduction to web page designing using HTML: create and save an HTML document, access a web page using a web browser.
- HTML tags: html, head, title, body, (attributes: text, background, bgcolor, link, vlink, alink), br (break), hr(horizontal rule), inserting comments, h1…h6 (heading), p (paragraph), b (bold), i (italics), u (underline), ul (unordered list), ol (ordered list), and li (list item). Description lists: dl, dt and dd. Attributes of ol (start, type), ul (type).
- Font tags (attributes: face, size, color).
- Insert images: img (attributes: src, width, height, alt), sup (super script), sub (subscript).
- HTML Forms: Textbox, radio buttons, checkbox, password, list, combobox.
- Embed audio and video in a HTML page.
- Create a table using the tags: table, tr, th, td, rowspan, colspan
- Links: significance of linking, anchor element (attributes: href, mailto), targets.
- Cascading style sheets: colour, background-colour, border-style, margin, height, width, outline, font (family, style, size), align, float.
Unit-3: Cyber ethics
- Netiquettes.
- Software licenses and the open source software movement.
- Intellectual property rights, plagiarism and digital property rights.
- Freedom of information and the digital divide.
- E-commerce: Privacy, fraud, secure data transmission.
Unit-4: Lab Exercises
- Create static web pages.
- Use style sheets to enforce a format in an HTML page (CSS).
- Embed pictures, audio and videos in an HTML page.
- Add tables and frames in an HTML page.
- Decorate web pages using graphical elements.
- Create a website using several webpages. Students may use any open source or proprietary tool.
- Work with HTML forms: text box, radio buttons, checkbox, password, list, combo box.
- Write a blog using HTML pages discussing viruses, malware, spam and antiviruses.
- Create a web page discussing plagiarism. List some reported cases of plagiarism and the consequent punishment meted out. Explain the nature of the punishment in different countries as per their IP laws.
What is Competency Based Education?
Competency-based Education (CBE) is an educational approach which allows students to grow as per their ability to master a skill or competency at their own pace regardless of the environment. It is an approach to teaching, learning, and assessment that focuses on students’ demonstration of learning outcomes and attaining proficiency in particular competencies in each subject.
This approach is modified to meet different learning abilities and can lead to more efficient student outcomes.
Key Features of CBE
- Equity for all students.
- Differentiated support based on students’ individual learning needs.
- Progress based on evidence of mastery rather than time in the classroom.
- The use of formative assessment, where students are encouraged to reflect on their own work and identify areas for improvement.
Benefits of CBE
- It integrates higher order thinking skills, interdisciplinary approaches and problem-solving as these are essential to the modern world and workplace.
- It helps in developing social and emotional skills.
- It enables learners to be competent not only in the national context but also the international labour market.
Competency-based Questions
- Competency-based Questions emphasises real-world applications of knowledge and skills, and the authenticity of the learning experience.
- Competency-based Questions, as per the CBSE, can be in the form of MCQs, Case-based Questions, Source-based Integrated Questions, Gap-filling, True-False, Short Answer Questions, Long Answer Questions or any other type.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Computer Applications Class 10 Assertion Reason
Q1: What are assertion-reason questions in Computer Applications?
A1: Assertion-reason questions present a statement (the assertion) and a corresponding explanation (the reason). Students must determine if each statement is true or false and assess if the reason correctly explains the assertion. This type of question tests understanding of concepts and the logical relationships between ideas, helping students to think critically about their knowledge.
Q2: How do students answer assertion-reason questions?
A2: Typically, assertion-reason questions require students to assess both statements and choose an option that best describes their relationship. For instance:
A: Both assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation.
B: Both assertion and reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation.
C: The assertion is true, but the reason is false.
D: The assertion is false, but the reason is true.
Q3: What skills are assessed through assertion-reason questions?
A3: These questions assess logical reasoning, critical thinking, and comprehension skills. They require students to understand the relationship between concepts and to apply their knowledge accurately, which is essential for higher-order thinking.
Q4: What are some tips for solving assertion-reason questions effectively?
A4: Read both statements carefully and separately.
Determine the truth value of each statement on its own.
Check if the reason logically explains or directly relates to the assertion.
Practice with examples to become familiar with the structure and logic.
Q5: Are assertion-reason questions difficult for students to answer?
A5: Assertion-reason questions can be challenging if students focus solely on memorization without understanding the concepts. However, with a strong grasp of the fundamentals, students can approach these questions more confidently. Practicing these types of questions regularly helps in building familiarity and accuracy.
Q6: Are assertion-reason questions the same as true-false questions?
A6: No, assertion-reason questions are more complex than true-false questions. While true-false questions only assess whether a statement is correct, assertion-reason questions require students to analyze the relationship between two statements and determine if one explains the other. This adds a layer of logical reasoning that true-false questions typically do not have.
Q7: What are common mistakes students make in assertion-reason questions?
A7: Common mistakes include:
Not fully understanding one or both statements.
Assuming a logical connection without carefully evaluating it.
Relying on memorization instead of understanding concepts.
Overlooking keywords in statements that change the meaning, such as “always” or “only.”
To avoid these mistakes, students should focus on comprehension and avoid rushing through questions.
Q8: Why are assertion-reason questions important for CBSE assessments?
A8: CBSE includes assertion-reason questions to foster analytical thinking, deeper comprehension, and conceptual understanding in students. These questions help students go beyond basic definitions, promoting a more rounded knowledge of the subject. This approach also aligns with CBSE’s focus on competency-based learning.


