Last Updated on May 15, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 9 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 9 science chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings.
| Chapter | Matter in Our Surroundings |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 9 |
| Subject | Science |
| Useful for | Class 9 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 9 Science Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Matter in Our Surroundings
Questions
Question 1:
The word ‘matter’ refers to everything in the universe that has mass and takes up space. States of matter are generally described on the basis of qualities that can be seen or felt. Three states of matter can be found in daily life: solid, liquid and gas.
Matter that feels hard and maintains a fixed shape is called a solid, matter that feels wet and maintains its volume but not its shape is called a liquid. Matter that can change both shape and volume is called a gas.
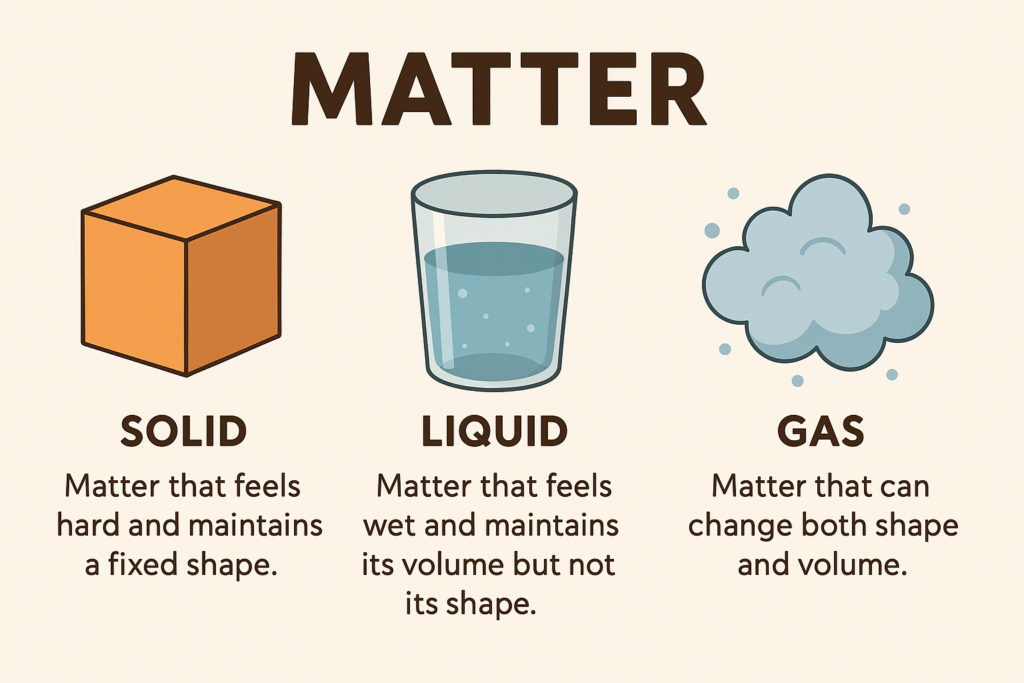
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions:
Q 1. In which form, do the water molecules have less kinetic energy?
a. Ice
b. Water
c. Steam
d. All of them have equal kinetic energy
Q2. Which of the following describes the liquid phase?
a. It has a definite shape and a definite volume.
b. It has a definite shape but not definite volume.
c. It has a definite volume but not a definite shape.
d. It has neither a definite shape nor a definite volume.
Q 3. Which one of the following statements is wrong for gases?
a. Gases do not have a definite shape and volume.
b. Volume of the gas is equal to the volume of the container confining the gas.
c. Confined gas exerts uniform pressure on the walls of container in all directions.
d. Mass of the gas cannot be determined by weighing a container in which it is enclosed.
Q 4. ‘Gases are easily compressed but liquids cannot be compressed.’ What can be inferred from this statement?
a. The forces of attraction between gas particles are stronger than that between liquid particles.
b. The gas particles are spaced further apart than liquid particles.
c. The gas particles have less energy than liquid particles.
d. The gas particles move more rapidly than liquid particles.
Q 5. As the solid melts to form liquid:
a. interparticle forces of attraction decrease
b. the kinetic energy of particles increases
c. compressibility increases
d. All of the above
Answers
1. (a) Ice
Explanation: Ice (solid) has less kinetic energy as compared to water (liquid) and steam (gas).
2. (c) It has a definite volume but not a definite shape.
3. (d) Mass of the gas cannot be determined by weighing a container in which it is enclosed.
Explanation: The mass of a gas can be determined by weighing the empty container first, then filling it with gas and again weighing the container filled with gas. The difference of two readings gives the mass of gas.
4. (b) The gas particles are spaced further apart than liquid particles.
Explanation: The large space between the particles of gas allow the gas to be easily compressed when pressure is applied.
5. (d) All of the above
Explanation: When a solid is heated, the interparticle force decreases and kinetic energy of the particles increases. Compressibility of liquids is slightly more than solids, hence increase
We hope the given case study question for Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 helps you in your learning.


Also check
Case study questions for other chapters of class 9 science is given below.
- Structure of the Atom Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 4
- Atoms and Molecules Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 12
- Sound Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11
- Work and Energy Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10
- Gravitation Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 9
- Force and Laws of Motion Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 8
- Motion Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 7
- Tissues Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
- The Fundamental Unit of Life Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 5
- Is Matter Around Us Pure Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
- Matter in Our Surroundings Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1
🚀 Boost Your Exam Prep: Get case study questions for all subjects (Class 6-12) now!
👉 Explore more resources on CBSE Class 9
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Matter and its physical properties
- Characteristics pf particles of mattter
- States of Matter
- Scales of Measuring Temperature
- Evaporation
- Factors affecting Rate of Evaporation
This chapter deals with the basic understanding of acids, bases, and salts, including their properties, reactions, pH scale, indicators, and practical applications.
Helpful Links for CBSE Class 9 Science Preparation
- Download Latest Sample Papers for CBSE Class 9 Science
- Download Worksheets for CBSE Class 9 Science
- Download Chapter Tests for CBSE Class 9 Science
- Download Case Study Question Bank for CBSE Class 9 Science
- Download Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 9 Physics
- Download Important MCQs for CBSE Class 9 Physics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Matter in Our Surroundings Case Study Questions
Q1: What are case study questions for CBSE examinations?
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 9 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 9 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on chemical reactions and equations for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on matter in our surroundings class 9 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of acids, bases and salts.
Q7: What is matter made up of?
A7: Matter is made up of particles.
Q8: What happens when salt is added to water?
A8: When we add salt in water, the particles of salt get into the spaces between particles of water. We say that salt has
been dissolved into water.
Q9: What happens when we light the incense stick in one corner of a room?
A9: The smell of the incense stick spreads throughout the room due to diffusion
Q10: Which of the following substances diffuses faster in a glass of water: a drop of honey or blue ink?
A10: Blue ink, because of the high kinetic energy of the particles of the given matter. Honey is viscous, and has low
kinetic energy.
Q11: Why does diffusion becomes faster on heating?
A11: On heating, the kinetic energy of the particles increases and the particles move faster. This speeds up the intermixing of particles
Q12: Why do the gases exert more pressure on the walls of the container than the solids?
A12: In gases, the particles move randomly at high speed and they collide with each other and with walls of the container.
Due to this collision with walls of the container, the gases exert more pressure than solids.
Q13: What happens to the particles of the solid during sublimation?
A13: Sublimation is a process in which the solid changes directly to gas either by decreasing pressure or increasing
temperature. A decrease in pressure increases the space between the particles and an increase in temperature
increase the kinetic energy of the particles.
Q14: List all the factors which affects the rate of evaporation.
A14: The factors affecting the rate of evaporation are:
(a) an increase in surface area
(b) an increase in temperature
(c) an increase in wind speed
(d) a decrease in humidity



