Last Updated on December 26, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 12 physics. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 12 physics. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 12 physics chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields.
| Chapter | Electric Charges and Fields |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Unit | Unit 1 Electrostatics |
| Useful for | Class 12 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Electric Charges and Fields
Questions
Question 1:
Surface charge density is defined as charge per unit surface area of surface charge distribution. i.e., $\sigma=\frac{d q}{d s}$. Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs having magnitude of $17.0 \times 10^{-22} \mathrm{Cm}^{-2}$ as shown. The intensity of electric field at a point is $E=\frac{\sigma}{\varepsilon_0}$, where $\varepsilon_0=$ permittivity of free space.
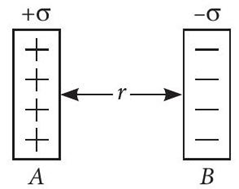
(i) $E$ in the outer region of the first plate is
(a) $17 \times 10^{-22} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(b) $1.5 \times 10^{-25} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(c) $1.9 \times 10^{-10} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(d) zero
(ii) $E$ in the outer region of the second plate is
(a) $17 \times 10^{-22} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(b) $1.5 \times 10^{-15} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(c) $1.9 \times 10^{-10} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(d) zero
(iii) $E$ between the plates is
(a) $17 \times 10^{-22} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(b) $1.5 \times 10^{-15} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(c) $1.9 \times 10^{-10} \mathrm{~N} / \mathrm{C}$
(d) zero
(iv) The ratio of $E$ from right side of $B$ at distances 2 cm and 4 cm , respectively is
(a) $1: 2$
(b) $2: 1$
(c) $1: 1$
(d) $1: \sqrt{2}$
(v) In order to estimate the electric field due to a thin finite plane metal plate, the Gaussian surface considered is
(a) spherical
(b) cylindrical
(c) straight line
(d) none of these
Answers
(i) Option (d) is correct.
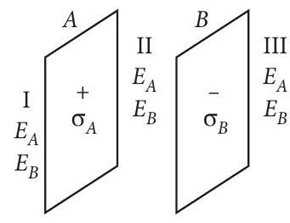
There are two plates $A$ and $B$ having surface charge densities,
$$
\sigma_A=17.0 \times 10^{-22} \mathrm{C} / \mathrm{m}^2
$$
on $A$ and $\sigma_B=-17.0 \times 10^{-22} \mathrm{C} / \mathrm{m}^2$ on $B$, respectively.
According to Gauss’ theorem, if the plates have same surface charge density but having opposite signs, then the electric field in region I is zero.
$$
E_{\mathrm{I}}=E_A+E_B=\frac{\sigma}{2 \varepsilon_0}+\left(-\frac{\sigma}{2 \varepsilon_0}\right)=0
$$
(ii) (d): The electric field in region III is also zero.
$$
E_{\mathrm{III}}=E_A+E_B=\frac{\sigma}{2 \varepsilon_0}+\left(-\frac{\sigma}{2 \varepsilon_0}\right)=0
$$
(iii) (c): In region II or between the plates, the electric field
$$
\begin{aligned}
& E_{\mathrm{II}}=E_A-E_B=\frac{\sigma}{2 \varepsilon_0}+\frac{\sigma}{2 \varepsilon_0} \\
&=\frac{\sigma\left(\sigma_A \text { or } \sigma_B\right)}{\varepsilon_0}=\frac{17.0 \times 10^{-22}}{8.85 \times 10^{-12}} \\
& E=1.9 \times 10^{-10} \mathrm{NC}^{-1}
\end{aligned}
$$
(iv) (c): Since, electric field due to an infinite-plane sheet of charge does not depend on the distance of observation point from the plane sheet of charge. So, for the given distances, the ratio of $E$ will be $1: 1$.
(v) (b): In order to estimate the electric field due to a thin finite plane metal plate, we take a cylindrical cross-sectional area $A$ and length $2 r$ as the gaussian surface.
Also check
Case study questions for other chapters of class 12 physics is given below.
- Semiconductor Electronics Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 14
- Nuclei Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 13
- Atoms Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 12
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 11
- Wave Optics Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 10
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 9
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 8
- Alternating Current Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 7
- Electromagnetic Induction Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 6
- Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 5
- Moving Charges and Magnetism Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 4
- Current Electricity Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 3
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 2
- Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 1
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics
We hope the given case study questions for Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 helps you in your learning.
Download eBooks for CBSE Class 12 Physics (Exam Special)
- 120 Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics
- 320 Assertion Reasoning Questions for Class 12 Physics
- 95 Reasoning Based Questions for Class 12 Physics
- Important Derivation for Class 12 Physics
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics
- Chapter Test for Class 12 Physics with Solutions
- 230 Important Numerical for Class 12 Physics
- 75 Important Diagrams & Graphs for Class 12 Physics
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Electric charges
- Conservation of charge
- Coulomb’s law – force between two-point charges
- Forces between multiple charges
- Superposition principle
- Continuous charge distribution
- Electric field
- Electric field due to a point charge
- Electric field lines
- Electric dipole
- Electric field due to a dipole
- Torque on a dipole in a uniform electric field
- Electric flux
- Statement of Gauss’s theorem
- Applications of Gauss’s theorem to find field due to:
Infinitely long straight wire
Uniformly charged infinite plane sheet
Uniformly charged thin spherical shell (field inside and outside)
Two electric field lines never cross each other. If they intersect, then there will be two directions of electric field at the point of intersection which is not possible.
For further practice on case study questions related to Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Physics, we recommend exploring the link given below.
Quiz
| Topic | Electric Charges and Fields |
| Useful for | CBSE Class 12 Students |
| Type of Questions | MCQs, Case Study, Assertion Reason |
| No. of Questions | 45 |
| Solutions | Instant Solutions after Completion of Quiz |
| Quiz Link | Click here to Take Test |
| Price | Free |
How to take quiz or test using the given link
It’s quite simple!
Step 1: Click on the given link. You will see the below screen.
Step 2: Fill in the necessary details. There is no need to register. Just fill your email and name and click on the button “Take Assessment”. The below screen will appear.
Step 3: Click on start assessment. Now you are ready to take test.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Electric Charges and Fields Case Study Questions
Q1: What are case study questions for CBSE examinations?
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 12 physics chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 12 physics chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on “Electric Charges and Fields” for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on “Electric Charges and Fields” class 12 physics into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of “Electric Charges and Fields”.
Q7: Electrostatic forces are much stronger than gravitational forces. Give one example.
A7: A charged glass rod can lift a piece of paper against the gravitational pull of the earth on this piece.
Q8: What is an electric line of force? What is its importance?
A8: An electric line of force is an imaginary straight or curved path along which a small positive test charge is supposed to move when free to do so.
The tangent at a point on an electric line of force gives the direction of the resultant electric field at that point.
The relative closeness of electric lines of force in a certain region provides us an estimate of the electric field strength in that region
Q9: Can a charged body attract another uncharged body? Explain.
A9: Yes, a charged body can attract another uncharged body. When the charged body is placed near the uncharged body, the induced charges of opposite kind are produced on the uncharged body and the uncharged body is attract by charged body.
Q10: In Coulomb’s law, on what factors the value of electrostatic force constant K depends?
A10: It depends on the nature of medium between the two charges and also on the system of units.
Q11: Is the mass of a body affected on charging?
A11: Yes, very slightly. The negatively charged body gains mass also along with electrons.
Q12: How does a free electron at rest move in an electric field?
A12: When the electron is released, it will move in a direction opposite to the direction of electric field.
Download Customised White Label Study Materials in MS Word Format
We are providing teaching resources to teachers and coaching institute looking for customised study materials in MS word format. Our High-quality editable study material which is prepared by the expert faculties are Highly useful for Teachers, Mentors, Tutors, Faculties, Coaching Institutes, Coaching Experts, Tuition Centers.



