Last Updated on May 18, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 11 Physics. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 11 Physics. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 11 Physics chapter 3 Motion in a Plane.
| Chapter | Motion in a Plane |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 11 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Useful for | Class 11 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 11 Physics Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Motion in a Plane
Case Study Question 1:
Projectile Motion – Ball Thrown from a Height
Passage:
A ball is projected with a speed of 20 m/s at an angle of 30° above the horizontal from the top of a building 25 m high. The student is asked to find the time of flight, maximum height from the ground, and range of the projectile. Air resistance is negligible.
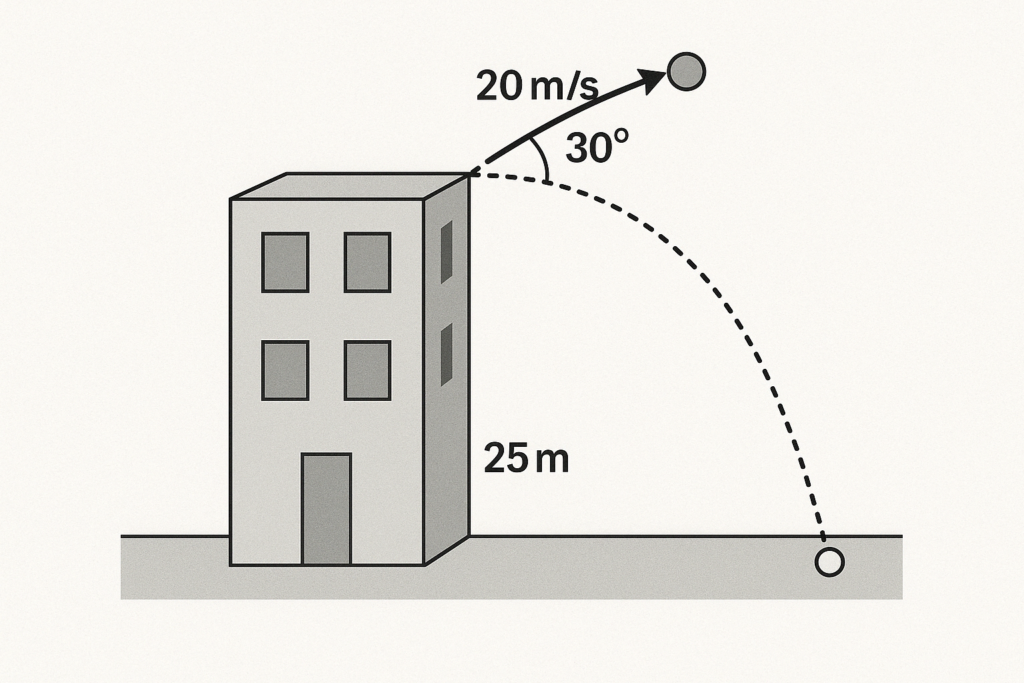
Q1. What is the horizontal component of the initial velocity?
(a) $10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
(b) $20 \cos 30^{\circ}$
(c) $20 \sin 30^{\circ}$
(d) $10 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
Q2. What is the time taken to reach the highest point (ignore height of building)?
(a) $\frac{20 \sin 30^{\circ}}{g}$
(b) $\frac{20 \cos 30^{\circ}}{g}$
(c) $\frac{10}{g}$
(d) $\frac{5}{g}$
Q3. Which of the following quantities remains constant throughout the motion (neglect air resistance)?
(a) Vertical velocity
(b) Horizontal velocity
(c) Acceleration in vertical direction
(d) Speed
Q4. Which of the following equations is best used to find the maximum height from the ground?
(a) $H=\frac{u^2 \sin ^2 \theta}{2 g}$
(b) $H=u t+\frac{1}{2} a t^2$
(c) $R=\frac{u^2 \sin 2 \theta}{g}$
(d) $v^2=u^2+2 a s$
Answers:
Q1. (b)
Q2. (a)
Q3. (b)
Q4. (a)
Case Study Question 2:
River Boat Problem
Passage:
A boat wants to cross a river flowing eastward with a speed of 4 m/s. The boat can row at 5 m/s in still water. The pilot aims the boat perpendicular to the river bank (i.e., due north). Students must calculate the actual path of the boat and the time taken to cross the river of width 100 m.
Q1. What is the boat’s velocity component perpendicular to the river (northward)?
(a) $4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
(b) $5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
(c) $3 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
(d) $\sqrt{5^2-4^2}$
Q2. How much time will the boat take to cross the river?
(a) 20 s
(b) 25 s
(c) 30 s
(d) 40 s
Q3. What will be the drift (distance carried away downstream) due to river flow?
(a) 20 m
(b) 80 m
(c) 100 m
(d) 0 m
Q4. What is the resultant speed of the boat with respect to the ground?
(a) $4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
(b) $5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
(c) $\sqrt{41} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
(d) $3 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
Answers:
Q1. (b)
Q2. $t=\frac{100}{5}=20 \mathrm{~s} \rightarrow$ (a)
Q3. Drift $=4 \times 20=80 \mathrm{~m} \rightarrow$ (b)
Q4. $\sqrt{5^2+4^2}=\sqrt{41} \approx 6.4 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} \rightarrow$ (c)
Case Study Question 3:
Uniform Circular Motion – Satellite Orbit
Passage:
A satellite is moving in a circular orbit of radius RRR around Earth. The centripetal force required for circular motion is provided by the gravitational force between the Earth and the satellite. The motion is uniform, but the velocity vector keeps changing due to the continuous change in direction.
Q1. What provides the necessary centripetal force in satellite motion?
(a) Tension
(b) Magnetic force
(c) Gravitational force
(d) Normal force
Q2. What is the direction of acceleration in uniform circular motion?
(a) Along the tangent
(b) Towards the center
(c) Away from the center
(d) Along the radius away from center
Q3. Which of the following remains constant in uniform circular motion?
(a) Velocity vector
(b) Speed
(c) Direction of motion
(d) Centripetal acceleration
Q4. If the speed of the satellite is doubled while keeping the same orbit radius, what will happen to the required centripetal force?
(a) Doubles
(b) Halves
(c) Becomes four times
(d) Remains unchanged
Answers:
Q1. (c)
Q2. (b)
Q3. (b)
Q4. (c)
We hope the given case study questions for Motion in a Plane Class 11 helps you in your learning.
Related Posts
👉 Motion in a Plane MCQ Questions
👉 Motion in a Plane Assertion Reason Questions
Also check
- Waves Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 14
- Oscillations Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 13
- Kinetic Theory Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 12
- Thermodynamics Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 11
- Thermal Properties of Matter Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 10
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 9
- Mechanical Properties of Solids Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 8
- Gravitation Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 7
- System of Particles and Rotational Motion Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 6
- Work, Energy and Power Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 5
- Laws of Motion Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 4
- Motion in a Plane Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 3
- Motion in a Straight Line Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 2
- Units and Measurements Class 11 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 1
🚀 Boost Your Exam Prep: Get case study questions for all subjects (Class 6-12) now!
👉 Explore more resources on CBSE Class 11
Download eBooks for CBSE Class 12 Physics (Exam Special)
- 120 Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics
- 320 Assertion Reasoning Questions for Class 12 Physics
- 95 Reasoning Based Questions for Class 12 Physics
- Important Derivation for Class 12 Physics
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics
- Chapter Test for Class 12 Physics with Solutions
- 230 Important Numerical for Class 12 Physics
- 75 Important Diagrams & Graphs for Class 12 Physics
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Scalars and vectors
- Projectile motion
- Relative velocity
- Motion in two dimensions
Projectile motion is a classic example of motion in two dimensions under constant acceleration.
For further practice on case study questions related to Motion in a Plane Class 11 Physics, we recommend exploring the link given below.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Motion in a Plane Case Study Questions
Q1: What are case study questions in Motion in a Plane?
A1: Case study questions in Motion in a Plane test your ability to apply concepts in real-life scenarios.
Q2: Are these questions asked in board exams?
A2: Yes, CBSE has started including case study/competency-based questions in final exams.
Q3: How should I prepare for case study questions?
A3: Focus on understanding concepts and practicing application-based problems.
Q4: Are answers provided for Class 11 Physics Motion in a Plane case study questions?
A4: Yes, detailed answers are provided for all questions.
Download Customised White Label Study Materials in MS Word Format
We are providing teaching resources to teachers and coaching institute looking for customised study materials in MS word format. Our High-quality editable study material which is prepared by the expert faculties are Highly useful for Teachers, Mentors, Tutors, Faculties, Coaching Institutes, Coaching Experts, Tuition Centers.



