Last Updated on November 16, 2025 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 12 physics. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 12 physics. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 12 physics chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics.
| Chapter | Semiconductor Electronics |
| Type of Questions | Case Study Questions |
| Nature of Questions | Competency Based Questions |
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | 12 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Unit | Unit 9 Electronic devices |
| Useful for | Class 12 Studying Students |
| Answers provided | Yes |
| Difficulty level | Mentioned |
| Important Link | Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Case Study |
Case Study Questions on Semiconductor Electronics
Questions
Question 1:
A silicon p-n junction diode is connected to a resistor R and a battery of voltage VB through milliameter (mA) as shown in figure. The knee voltage for this junction diode is VN = 0.7 V. The p-n junction diode requires a minimum current of 1 mA to attain a value higher than the knee point on the V-I characteristics of this junction diode. Assuming that the voltage V across the junction is independent of the current above the knee point.
A p-n junction is the basic building block of many semiconductors, devices like diodes. Important process occurring during the formation of a p-n junction are diffusion and drift. In an n-type semiconductor concentration of electrons is more as compared to holes. In a p-type semiconductor, concentration of holes is more as compared to electrons.
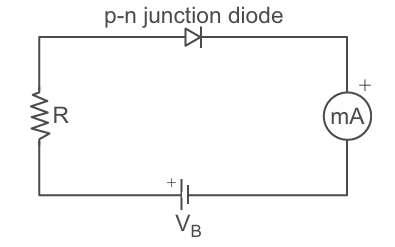
Read the given passage carefully and give the answer of the following questions:
Q 1. If VB = 5 V, then what will be the maximum value of R so that the voltage V is above the knee point voltage?
Q 2. If VB = 5 V, then what will be the value of R in order to establish a current to 6 mA in the circuit?
Q 3. When the diode is reverse biased with a voltage of 6 V and Vbi = 0.63 V, calculate the total potential.
Q 4. If VB = 6 V, then calculate the power dissipated in the resistor R, when a current of 6 mA flows in the circuit.
Answers
1. Voltage drop across $R$,
$$
V_R=V_B-V_N=5-0.7=4.3 \mathrm{~V}
$$
Given, $\quad I_{\text {min }}=1 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~A}$
Maximum value of resistance,
$$
\begin{aligned}
& R_{\max }=\frac{V_R}{I_{\min }}=\frac{4.3}{1 \times 10^{-3}} \\
& \quad=4.3 \times 10^3 \Omega=4.3 \mathrm{k} \Omega
\end{aligned}
$$
2. Given,
$$
\begin{aligned}
I & =6 \mathrm{~mA}=6 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~A}_i \\
V_R & =V_B-V_N=5-0.7=4.3 \mathrm{~V} \\
R & =\frac{V_R}{I}=\frac{4.3}{6 \times 10^{-3}}=717 \Omega
\end{aligned}
$$
3. Total potential, $V_t=V_{b i}+V_R=0.63+6=6.63 \mathrm{~V}$
4. Given, $V_B=6 \mathrm{~V} ; V_N=0.7 \mathrm{~V}, V_R=6-0.7=5.3 \mathrm{~V}$
Power dissipated, $P=I \times V_R=\left(6 \times 10^{-3}\right) \times 5.3$
$$
=31.8 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~W}=31.8 \mathrm{~mW}
$$
Also check
Case study questions for other chapters of class 12 physics is given below.
- Semiconductor Electronics Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 14
- Nuclei Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 13
- Atoms Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 12
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 11
- Wave Optics Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 10
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 9
- Electromagnetic Waves Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 8
- Alternating Current Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 7
- Electromagnetic Induction Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 6
- Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 5
- Moving Charges and Magnetism Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 4
- Current Electricity Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 3
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 2
- Electric Charges and Fields Class 12 Case Study Questions Physics Chapter 1
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics
We hope the given case study questions for Semiconductor Electronics Class 12 helps you in your learning.
Download eBooks for CBSE Class 12 Physics (Exam Special)
- 120 Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physics
- 320 Assertion Reasoning Questions for Class 12 Physics
- 95 Reasoning Based Questions for Class 12 Physics
- Important Derivation for Class 12 Physics
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics
- Chapter Test for Class 12 Physics with Solutions
- 230 Important Numerical for Class 12 Physics
- 75 Important Diagrams & Graphs for Class 12 Physics
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Energy Bands in Conductors, Semiconductors, and Insulators (Qualitative Ideas Only)
- Intrinsic and Extrinsic Semiconductors
- p-type and n-type Semiconductors
- p-n Junction
- Semiconductor Diode
- I-V Characteristics in Forward and Reverse Bias
- Application of Junction Diode
- Diode as a Rectifier
A semiconductor acts like an ideal insulator at absolute zero temperature (0 K). It is because the free electrons in the valence band of semiconductors will not carry enough thermal energy to overcome the forbidden energy gap at absolute zero.
For further practice on case study questions related to Semiconductor Electronics Class 12 Physics, we recommend exploring the link given below.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Semiconductor Electronics Case Study Questions
Q1: What are case study questions for CBSE examinations?
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 12 physics chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 12 physics chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on “Semiconductor Electronics” for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on “Semiconductor Electronics” class 12 physics into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of “Semiconductor Electronics”.
Q7: By which charge carriers, an intrinsic semiconductor will have conduction?
A7: Electrons and holes.
Q8: How does the resistance of a semiconductor change when heated?
A8: With increase in temperature, a greater number of bonds inside the semiconductor are broken.
Q9: How does an increase in doping concentration affect the width of depletion layer of a p-n junction diode?
A9: The width of depletion layer of a p-n junction diode decreases on an increase in doping concentration.
Q10: What are the two types of semiconductors on the basis of purity?
A10: On the basis of purity, semiconductor can be classified as:
(i) intrinsic semiconductors
(ii) extrinsic semiconductors
Download Customised White Label Study Materials in MS Word Format
We are providing teaching resources to teachers and coaching institute looking for customised study materials in MS word format. Our High-quality editable study material which is prepared by the expert faculties are Highly useful for Teachers, Mentors, Tutors, Faculties, Coaching Institutes, Coaching Experts, Tuition Centers.



