Last Updated on February 21, 2025 by sanjjeett
The NCERT Solutions have been updated for 2024-2025 sessions, with the new NCERT Books. All questions are solved with detailed explanation of each and every questions. In this article, we are providing NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Conservation of Plants and Animals. It is a part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science series.
| Chapter | Conservation of Plants and Animals |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Type of Material | NCERT Solutions |
| Format | Question-Answer Format |
| Class | 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Useful for | Class 8 Studying Students |
| Session | 2024-25 |
| No. of Intext Questions | 9 |
| Exercise Questions | 7 |
| Solutions provided | Yes |
| Important Link | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science |
Conservation of Plants and Animals NCERT Solutions Class 8
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4, Combustion and Flame, offer clear, step-by-step answers to all textbook questions. Expertly crafted, these solutions simplify complex concepts, enhance understanding, and build confidence, helping students excel in their studies.
Intext Questions
Page-53
Q. 1. Paheli is curious to know the purpose of making national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves.
Ans. To conserve and preserve the animals and plants whose numbers are diminishing and are facing extinction, national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves are established for the same purpose.
Q. 2. Boojho is curious to know how deforestation reduces rainfall on the one hand and leads to floods on the other.
Ans. Deforestation leads to global warming which increases the temperature of the earth and this increase in temperature disturbs the water cycle and reduces rainfall. Deforestation also leads to a decrease in the water holding capacity of soil and the movement of water from the soil surface into the ground, which causes floods.
Page-57
Q. 3. Paheli has heard that some of the endemic species may vanish. Is it true?
Ans. Yes, the destruction of habitat, increasing popula tion and introduction of new species may affect the natural habitat of endemic species and endanger their existence.
Page-58
Q. 4. Boojho wants to know the difference between a zoo and a wildlife sanctuary.
Ans. Both wildlife sanctuary and zoo are the places where animals are protected and preserved. But wildlife sanctuary provides natural habitat while in zoo, animals live in artificial atmosphere.
Page-59
Q. 5. Boojho wants to know whether tigers are still found in the forest. He is excited to see a tiger.
Ans. Tiger is one of the many species which are slowly disappearing from our forests. But, the Satpura tiger reserve is unique in the sense that a significant increase in the population of tiger has been seen here.
Q. 6. Paheli wants to know whether only big animals are facing the danger of extinction.
Ans. No, the small animals are much more in danger than the bigger animals. At times, we kill snakes, frogs, lizards, bats and owls ruthlessly without realising their importance in the ecosystem. By killing them we are harming ourselves. They might be small in size but their role in the ecosystem cannot be ignored. They form part of food webs.
Page-60
Q. 7. Boojho wonders if there is a record of the endangered species!
Ans. Red Data Book is the source book which keeps a record of all endangered animals and plants. There are different Red Data Books for plants, animals and other different species.
Q. 8. Paheli is curious to know what would happen if we had no wood. Is there any alternative available for wood? Boojho says that paper is one of the important products we get from forests. Boojho asks whether there are any alternatives available for paper.
Ans. If there is no wood, then we will not receive fuels and many other things used for domestic purposes such as paper, matchsticks, furniture, etc. Being digital may be an alternative for paper.
Q. 9. Boojho wants to know if there is any permanent solution for the problem of deforestation
Ans. The answer to deforestation is reforestation, which is restocking of the destroyed forests by planting new trees.
Exercise Questions
Q. 1. Fill in the blanks:
(i) A place where animals are protected in their natural habitat is called ________.
(ii) Species found only in a particular area are known as ________.
(iii) Migratory birds fly to far places because of _________ changes.
Ans. (i) wildlife sanctuary, (ii) endemic species, (iii) climatic
Q. 2. Differentiate between the following:
(i) Wildlife Sanctuary and Biosphere Reserve
(ii) Zoo and Wildlife Sanctuary
(iii) Endangered and Extinct Species
(iv) Flora and Fauna
Ans. (i)
| Wildlife Sanctuary | Biosphere Reserve |
|---|---|
| Wildlife Sanctuaries provide protection and suitable living conditions to wild animals. | Large areas of protected land for conservation of wild life, plant and animal resources and traditional life of the tribals living in the area. |
| Preserves wild animals and birds. | Preserves complete biodiversity including plants, animals and microorganisms. |
| Certain activities such as grazing livestock, collecting medicinal plants and firewood is allowed. | Human activities are not allowed. |
| Examples – Sanjay Gandhi Wildlife Sanctuary, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary | Examples – Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve, Sunderbans National Reserve |
(ii)
| Zoo | Wildlife sanctuary |
|---|---|
| Animals are kept in artificial habitat. | Animals are kept in their natural habitat. |
| Animals are kept for public display. | Animals are protected in their own environment. |
| Zoo contains the animals that are brought from the different parts of the world for exhibition. | A wildlife sanctuary contains the animals that are found locally in that area. |
| Examples – Mysore Zoo | Examples – Sanjay Gandhi Wildlife Sanctuary |
(iii)
| Endangered species | Extinct species |
|---|---|
| Animals/plants whose numbers are diminishing to a level that they might face extinction are known as the endangered animals. | Animals/plants that no more exist on earth are called extinct species. |
| Can be saved by efforts of conservation. | Cannot be revived. |
| Examples – African wild dog, Royal Bengal tiger | Examples – Dodo, Dinosaurs |
(iv)
| Flora | Fauna |
|---|---|
| Flora means the plants naturally occurring in a particular area. | Fauna means the animals naturally living in a particular area. |
| Flora is the naturally grown greenery of a region. | Fauna includes all types of organisms from tiny bacteria to giant animals. |
| Flora can make their own food with the help of photosynthesis. | Fauna can’t make their own food, they depend on plants for their food. |
| Some examples of flora: mosses, herbs, shrubs and trees etc. | Some examples of fauna: birds, animals, fish, insects, etc. |
Q. 3. Discuss the effects of deforestation on the
following: (Medium)
(i) Wild animals
(ii) Environment
(iii) Villages (Rural areas)
(iv) Cities (Urban areas)
(v) Earth
(vi) The next generation
Ans. (i) The effects of deforestation on wild animals are:
- Deforestation leads to the loss of shelter, food sources, and breeding grounds for wild animals.
- They are forced to migrate to urban areas in search of food and shelter leading to their clash with humans and exposing them to various threats.
- Deforestation often results in the death of many wild animals gradually leading to their extinction.
(ii) Following are the effects of deforestation on Environment:
- It increases the temperature and pollution level on the earth.
- Ground water level gets lowered.
- Rainfall decreases.
- Fertility of soil decreases.
- Higher carbon dioxide results in global warming.
(iii) The effects of deforestation on Villages (Rural areas) are:
- Deforestation results in loss of shelter of wild animals. These animals often enter the nearby villages and pose a threat to villagers.
- Villagers depend on forest products like wood, honey, resins etc. for their livelihood. Deforestation gives them economical set back.
- Deforestation causes soil erosion and floods that decrease the fertility of soil hampering agricultural activities in rural areas.
(iv) The effects of deforestation on Cities (Urban areas) are:
- Rise in temperature due to global warming.
- Reduction in rainfall.
- Increased pollution.
- Increased risk of many natural calamities such as floods and droughts.
- Deteriorating water quality and availability.
(v) The effects of deforestation on Earth are:
- Climate change: Untimely rainfall, frequent droughts and heat waves are a few effects of climate change.
- Desertification: Removal of the top layer of the soil exposes the lower, hard and rocky layers. This soil has less humus and is less fertile. Gradually the fertile land gets converted into deserts.
- Soil erosion: Deforestation leaves the land naked and this causes large scale loss of top fertile layer of soil.
- Flooding: The barren lands are more susceptible to flooding.
- Global warming: Destruction of forest results in accumulation of green house gases leading to global warming.
(vi) The effects of deforestation on the next generation will be:
- The next generation will likely face more extreme weather events, rising temperatures, and other climate-related challenges, impacting their quality of life.
- The next generation will lose biodiversity we are having today. Many species might go extinct before the next generation has a chance to understand and appreciate them.
- The next generation will face shortage of essential natural resources like wood, clean water, and medicinal plants.
- Increased pollution will affect air and water quality, leading to respiratory problems, waterborne diseases, and other health concerns for the next generation.
- Climatic changes and extinction of animals will lead to food scarcity for the next generation.
Q. 4. What will happen if:
(Medium)
(i) we go on cutting trees?
(ii) the habitat of an animal is disturbed?
(iii) the top layer of soil is exposed?
Ans. (i) If we go on cutting trees, we will face the problem of food, wood, shelter, etc. Also, the cutting of trees leads to the decrease in level of oxygen and also causes global warming.
(ii) If the habitat of an animal is disturbed the animal will face extinction and survival becomes very difficult for it.
(iii) The exposed layer has less humus and is less fertile. Gradually, the fertile land can convert into deserts. It is called deforestation.
Q. 5. Answer in brief:
(Medium)
(i) Why should we conserve biodiversity?
(ii) Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals. Why?
(iii) Some tribes depend on the jungle. How?
(iv) What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
(v) What is Red Data Book?
(vi) What do you understand by the term migration?
Ans. (i) Biodiversity refers to the variety in life existing on earth, their inter-relationships and their relationship with the environment. So, if biodiversity is not conserved, it will cause disbalancing of life-cycles on earth.
(ii) Wild animals are killed or captured by man for various purposes, so only the protection of forests is not completely safe for wild animals.
(iii) Some tribes still live in the jungle. The forests provide them food and economical support. By selling the wood and products of forests, they earn money. These tribes depend only on growth of forest.
(iv) Causes: The forests or trees are cut for procuring land for cultivation, building houses and factories, making furniture or using it as fuel. Also, some natural processes such as forest fires and severe drought cause the deforestation.
Consequences: The deforestation increases the temperature and pollution level on the earth. It decreases the level of oxygen in the atmosphere and ground water level is also lowered. Deforestation disturbs the balance in nature. If continuous cutting of trees would continue, rainfall and the fertility of the soil will be affected. As a result, there are increased chances of natural calamities such as floods and drought.
(v) Red Data Book: Red Data Book is the source book which keeps record of all endangered animals and plants. There are different Red Data Books for plants, animals and other different species.
(vi) Migration: It is the change of location of birds to far away specific areas due to climatic changes every year during a particular time. These birds fly for laying eggs as the weather in their natural habitat becomes very cold and inhospitable. Birds who cover long distance to reach another land are known as the migratory birds.
Q. 6. In order to meet the ever-increasing demand in factories and for shelter, trees are being continually cut. Is it justified to cut trees for such projects?
Ans. No, cutting of trees leads to many problems as global warming, desertification, drought, less rainfall, decrease in ground water level and oxygen, etc.
Q. 7. How can you contribute to the maintenance of green wealth of your locality? Discuss in your class and make a list of actions to be taken by you.
Ans. If we have to maintain our green wealth for generations, plantation of more trees is the only option. We should plant at least ten trees per year for cutting the effect of deforestation. Also, we should use other options of fuel instead of wood, which also helps us to stop the pollution.
Q.8. Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
Ans. The plants need carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Fewer trees would mean less consumption of carbon dioxide and its increased amount in the atmosphere. This leads to global warming as carbon dioxide traps the heat of sun rays. The increase in temperature on earth disturbs the water cycle and reduces rainfall. This causes drought.
Q.9. Find out about the national parks in your state. Identify and show their location on the outline map of India.
Ans. Student’s response.
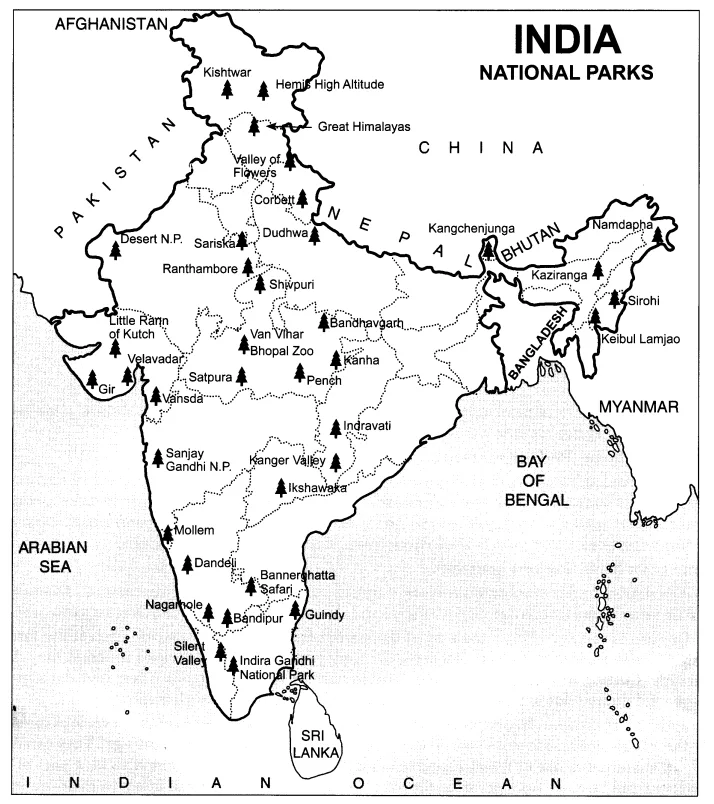
Q. 10. Why should paper be saved? Prepare a list of ways by which you can save paper.
Ans. Paper should be saved because it takes around 17 full-grown trees to make one tonne of paper. Trees are important to maintain a balance of nature. Therefore, in order to save trees and prevent the impact of their loss on living world, we need to save paper.
We can save paper by following ways
(i) Paper should be recycled.
(ii) Use both sides of a paper for writing purpose.
(iii) Spread awareness regarding the value of saving paper.
Q. 11. Complete the word puzzle:
Down:
- Species on the verge of extinction.
- A book carrying information about endangered species.
- Consequence of deforestation.
Across:
- Species which have vanished.
- Species found only in a particular habitat.
- Variety of plants, animals and microorganisms found in an area.
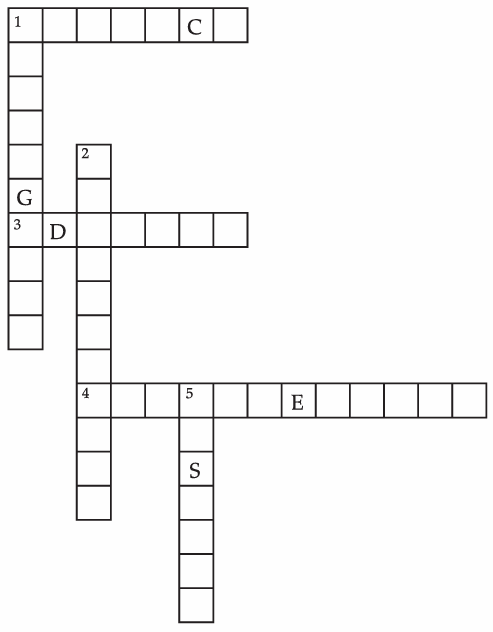

Ans. Down:
- Endangered 2. Red Data Book
- Disturb
Across:
- Extinct 3. Endemic
- Biodiversity
Related posts
| Conservation of Plants and Animals Case Study Questions | Conservation of Plants and Animals Assertion Reasoning |
Also check
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Force and Pressure
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Reproduction in Animals
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Combustion and Flame
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Coal and Petroleum
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
🔗 Explore More: Find all NCERT solutions here → NCERT Solutions for Class 1 to 12
You may also like
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Conservation of Plants and Animals Class 8 NCERT Solutions
Q1: What are NCERT Solutions?
A1: NCERT Solutions are detailed, step-by-step answers to the questions provided in the NCERT textbooks. They are designed to help students understand the concepts thoroughly and prepare effectively for their exams.
Q2: Why are NCERT Solutions important for students?
A2: NCERT Solutions are crucial for students because they offer clear explanations and step-by-step guidance on solving textbook problems. They help in building a strong foundation in each subject, making it easier for students to grasp complex concepts and perform well in their exams.
Q3: Are the NCERT Solutions available for free on Xam Content?
A3: Yes, all the NCERT Solutions on our website are available for free. We believe in making education accessible to all students, ensuring that everyone can benefit from our resources without any cost.
Q4: How can NCERT Solutions help in exam preparation?
A4: NCERT Solutions help in exam preparation by providing thorough explanations and solutions to textbook problems. They ensure that students understand the core concepts and are well-prepared for any type of question that may appear in their exams.
Q5: Are NCERT solutions enough for scoring good marks in Class 8 Science exams?
A5: Yes, NCERT solutions cover the entire syllabus prescribed by CBSE for Class 8 Science. If students thoroughly understand and practice these solutions, they can definitely score well in their exams. However, it’s also beneficial to supplement your studies with additional reference materials and practice questions. For various types of questions asked in social science exam, you can visit xamcontent.com.

