Last Updated on February 21, 2025 by sanjjeett
The NCERT Solutions have been updated for 2024-2025 sessions, with the new NCERT Books. All questions are solved with detailed explanation of each and every questions. In this article, we are providing NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Combustion and Flame. It is a part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science series.
| Chapter | Combustion and Flame |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Type of Material | NCERT Solutions |
| Format | Question-Answer Format |
| Class | 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Useful for | Class 8 Studying Students |
| Session | 2024-25 |
| No. of Intext Questions | 9 |
| Exercise Questions | 7 |
| Solutions provided | Yes |
| Important Link | NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science |
Combustion and Flame NCERT Solutions Class 8
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4, Combustion and Flame, offer clear, step-by-step answers to all textbook questions. Expertly crafted, these solutions simplify complex concepts, enhance understanding, and build confidence, helping students excel in their studies.
Intext Questions
Page-40
Q. 1. Boojho: We were told that food is a fuel for our body. Why?
Ans. Because in our body food is broken down by reaction with oxygen and energy is produced.
Page-42
Q. 2. Boojho: We have read that the sun produces heat and light. Is that through a combustion process?
Paheli: How can it be? There is no air in the sun.
Ans. In the sun, heat and light are produced by nuclear reactions.
Page-44
Q. 3. Why is it important to know the telephone numbers of the fire service?
Ans. It is important so that the fire brigade arrives on time and extinguishes the fire soon.
Page-49
Q. 4. Why are we advised never to sleep in a room with burning coal fire in it?
Ans. We are advised never to sleep in a room with burning coal fire because incomplete combustion of these fuels gives carbon monoxide gas. It is a very poisonous gas; it can kill persons sleeping in that room.
Exercise Questions
Q. 1. List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Ans. Necessary conditions are as follows:
(i) There must be proper supply of oxygen.
(ii) Presence of combustible substance.
(iii) Attainment of ignition temperature.
Q. 2. Fill in the blanks.
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes __________of air.
(b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is __________
(c) Fuel must be heated to its __________before it starts burning.
(d) The fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by __________
Ans. (i) pollution, (ii) kerosene, (iii) ignition temperature, (iv) water.
Q. 3. Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Ans. The combustion of fuels such as coal, petrol and diesel results in the production of unburnt carbon particles and carbon monoxide gas, both of which are harmful pollutants that can enter the air and contribute to respiratory diseases. In contrast, Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) generates these harmful by-products in very less quantities, making it a cleaner fuel option. Consequently, the adoption of CNG has played a role in reducing pollution levels in our cities.
Q. 4. Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Ans.
| S.No. | LPG | Wood |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | LPG is a gaseous fuel. | Wood is a solid type of fuel. |
| 2. | LPG doesn’t produce smoke and causes less pollution. | Wood produces lots of smoke and causes more pollution. |
| 3. | No cutting of trees is required to produce LPG. | Wood is obtained by cutting trees which leads to deforestation. |
| 4. | LPG has a higher calorific value of 55000 kJ/kg. | Wood has a lower calorific value ranging between 17000 and 22000 kJ/kg. |
| 5. | LPG is easier to store and transport. | Wood requires a lot of storage space and transport is difficult due to more weight. |
| 6. | Ignition temperature of LPG is low. | Ignition temperature of wood is high. |
Q. 5. Give reasons.
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
Ans. (a) If electrical equipment is on fire, water being a good conductor, may conduct electricity and harm those trying to douse the fire. Hence, water is not a good alternative to stop such fires. Instead, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the best extinguisher of fires involving electrical equipment.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood because :
- LPG doesn’t produce smoke and causes less pollution. Wood on the other hand produces lots of smoke and causes more pollution.
- No cutting of trees is required to produce LPG whereas wood is obtained by cutting trees which leads to deforestation.
- LPG has a higher calorific value of 55000 kJ/kg whereas wood has a lower calorific value ranging between 17000 and 22000 kJ/kg.
- LPG is easier to store and transport whereas wood requires a lot of storage space and transport is difficult due to more weight.
- Ignition temperature of LPG is low and that of wood is high.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily because it has low ignition temperature. When a piece of paper is wrapped around an aluminium pipe and heated, its ignition temperature is not attained so soon because the heat supplied is absorbed by the aluminium pipe. Hence, it does not catch fire easily.
Q. 6. Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Ans.
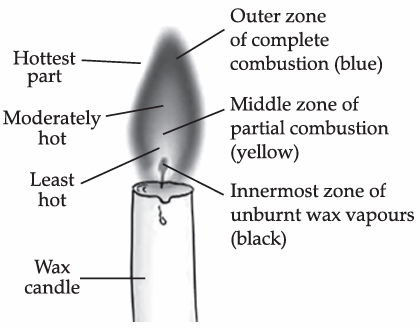
Q. 7. Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
Ans. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in terms of kilojoules per kg (kJ/kg).
Q. 8. Explain how CO2 is able to control fires.
Ans. Actually, CO2 cuts off the supply of air to the combustible substance or it brings down the temperature of the combustible substance below its ignition temperature by forming a layer on that substance which stops the fire.
Q. 9. It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Ans. As dry leaves have low ignition temperature than heap of green leaves because green leaves have water and other elements in them. So, to ignite the green leaves, we have to heat them up to the ignition temperature of their constituents which is comparatively high. So, it is easier to ignite dry leaves than green leaves.
Q. 11. In an experiment 4.5 kg of fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measured to be 1,80,000 kJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Ans. Given: Mass of fuel = 4.5 kg
The heat produced by combustion of 4.5 kg of fuel
= 1,80,000 kJ
So, the calorific value of fuel = Heat produced by
combustion of 1 kg of fuel
= 1,80,000 / 4.5 kJ/kg.
= 40,000 kJ/kg.
Q. 12. Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Ans. Rusting is the process in which metal reacts with oxygen of air and moisture of air and forms its oxides, which appear on the surface of that metal. While combustion is the process of burning of combustible substances in the presence of oxygen of the air. So, we cannot call the rusting as combustion.
Q. 13. Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Ans. As outermost flame is hotter than the middle part or the yellow flame,so the water of Ramesh will be heated in a shorter time.
Related posts
| Combustion and Flame Case Study Questions | Combustion and Flame Assertion Reasoning |
Also check
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 8 Force and Pressure
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 7 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 6 Reproduction in Animals
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 5 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 4 Combustion and Flame
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 3 Coal and Petroleum
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
🔗 Explore More: Find all NCERT solutions here → NCERT Solutions for Class 1 to 12
You may also like
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Combustion and Flame Class 8 NCERT Solutions
Q1: What are NCERT Solutions?
A1: NCERT Solutions are detailed, step-by-step answers to the questions provided in the NCERT textbooks. They are designed to help students understand the concepts thoroughly and prepare effectively for their exams.
Q2: Why are NCERT Solutions important for students?
A2: NCERT Solutions are crucial for students because they offer clear explanations and step-by-step guidance on solving textbook problems. They help in building a strong foundation in each subject, making it easier for students to grasp complex concepts and perform well in their exams.
Q3: Are the NCERT Solutions available for free on Xam Content?
A3: Yes, all the NCERT Solutions on our website are available for free. We believe in making education accessible to all students, ensuring that everyone can benefit from our resources without any cost.
Q4: How can NCERT Solutions help in exam preparation?
A4: NCERT Solutions help in exam preparation by providing thorough explanations and solutions to textbook problems. They ensure that students understand the core concepts and are well-prepared for any type of question that may appear in their exams.
Q5: Are NCERT solutions enough for scoring good marks in Class 8 Science exams?
A5: Yes, NCERT solutions cover the entire syllabus prescribed by CBSE for Class 8 Science. If students thoroughly understand and practice these solutions, they can definitely score well in their exams. However, it’s also beneficial to supplement your studies with additional reference materials and practice questions. For various types of questions asked in social science exam, you can visit xamcontent.com.

